The p53-p21WAF1 checkpoint pathway plays a protective role in preventing DNA rereplication induced by abrogation of FOXF1 function
- PMID: 21964066
- PMCID: PMC3205208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.09.017
The p53-p21WAF1 checkpoint pathway plays a protective role in preventing DNA rereplication induced by abrogation of FOXF1 function
Abstract
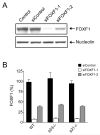
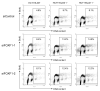
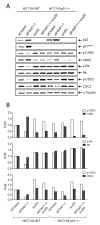
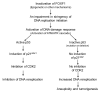
We previously identified FOXF1 as a potential tumor suppressor gene with an essential role in preventing DNA rereplication to maintain genomic stability, which is frequently inactivated in breast cancer through the epigenetic mechanism. Here we further addressed the role of the p53-p21(WAF1) checkpoint pathway in DNA rereplication induced by silencing of FOXF1. Knockdown of FOXF1 by small interference RNA (siRNA) rendered colorectal p53-null and p21(WAF1)-null HCT116 cancer cells more susceptible to rereplication and apoptosis than the wild-type parental cells. In parental HCT116 cells with a functional p53 checkpoint, the p53-p21(WAF1) checkpoint pathway was activated upon FOXF1 knockdown, which was concurrent with suppression of the CDK2-Rb cascade and induction of G(1) arrest. In contrast, these events were not observed in FOXF1-depleted HCT116-p53-/- and HCT116-p21-/- cells, indicating that the p53-dependent checkpoint function is vital for inhibiting CDK2 to induce G(1) arrest and protect cells from rereplication. The pharmacologic inhibitor (caffeine) of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (ATR) protein kinases abolished activation of the p53-p21(WAF1) pathway upon FOXF1 knockdown, suggesting that suppression of FOXF1 function triggered the ATM/ATR-mediated DNA damage response. Cosilencing of p53 by siRNA synergistically enhanced the effect of FOXF1 depletion on the stimulation of DNA rereplication and apoptosis in wild-type HCT116. Finally, we show that FOXF1 expression is predominantly silenced in breast and colorectal cancer cell lines with inactive p53. Our study demonstrated that the p53-p21(WAF1) checkpoint pathway is an intrinsically protective mechanism to prevent DNA rereplication induced by silencing of FOXF1.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

