Corticosteroids in the treatment of alcohol-induced rhabdomyolysis
- PMID: 21964178
- PMCID: PMC3184031
- DOI: 10.4065/mcp.2011.0102
Corticosteroids in the treatment of alcohol-induced rhabdomyolysis
Erratum in
- Mayo Clin Proc. 2012 Aug;87(8):810
Abstract
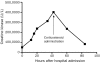
Rhabdomyolysis is a common condition with potentially devastating complications, including acute renal failure, arrhythmias, and death. The standard of care is to use supportive measures such as aggressive fluid repletion to prevent kidney injury and attenuate clinical symptoms. Besides fluid management, few therapeutic options are available for the treatment of acute rhabdomyolysis. As a result, acute and refractory cases remain difficult to manage. We report a case of alcohol-induced rhabdomyolysis that responded dramatically to high-dose corticosteroids. A 55-year-old man presented to the emergency department for evaluation of diffuse muscle pain, weakness, and darkening urine. On admission, his creatine kinase (CK) level was 50,022 U/L. Despite aggressive fluid repletion, his CK level continued to increase, peaking at 401,280 U/L with a concomitant increase in muscle pain and urine darkening. On administration of high-dose corticosteroids, clinical symptoms and CK levels improved dramatically, and the patient was discharged 36 hours later with complete resolution of muscle pain and weakness. Given their low toxicity profile, short-term high-dose corticosteroids may be a valid treatment option for recurrent rhabdomyolysis unresponsive to fluid repletion.
Figures
Comment in
-
Incomplete reporting in a case report of corticosteroids in the treatment of alcohol-induced rhabdomyolysis.Mayo Clin Proc. 2012 Aug;87(8):803. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.06.009. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012. PMID: 22862868 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Incomplete reporting in a case report of corticosteroids in the treatment of alcohol-induced rhabdomyolysis.Mayo Clin Proc. 2012 Aug;87(8):803. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.06.009. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012. PMID: 22862868 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
High Creatine Kinase Levels in Viral Myositis: A Case of Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Renal Failure.Am J Case Rep. 2025 Mar 29;26:e946551. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.946551. Am J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40156825 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term High-Dose Steroid Therapy in a Case of Rhabdomyolysis Refractory to Intravenous Fluids.Am J Case Rep. 2017 Oct 17;18:1110-1113. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.905196. Am J Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29055965 Free PMC article.
-
Non-traumatic rhabdomyolysis: Background, laboratory features, and acute clinical management.Clin Biochem. 2017 Aug;50(12):656-662. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.02.016. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Clin Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28235546 Review.
-
Rhabdomyolysis: A syndrome to be considered.Med Clin (Barc). 2022 Mar 25;158(6):277-283. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2021.09.025. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Med Clin (Barc). 2022. PMID: 34872769 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
A case of corticosteroid-responsive SARS-CoV-2 related massive rhabdomyolysis.IDCases. 2020;22:e00946. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00946. Epub 2020 Sep 4. IDCases. 2020. PMID: 32901220 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal patterns of cytokine and injury biomarkers in hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated with methylprednisolone.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1229611. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1229611. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37662953 Free PMC article.
-
Severe case of rhabdomyolysis following jellyfish envenomation in the Mediterranean Sea.RMD Open. 2023 Nov;9(4):e003569. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003569. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37945287 Free PMC article.
-
Nontraumatic rhabdomyolysis with short-term alcohol intoxication - a case report.Clin Case Rep. 2015 Oct;3(10):769-72. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.326. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Clin Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26509002 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory rhabdomyolysis responsive to corticosteroid therapy.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020 Dec 14;34(2):314-315. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1851627. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020. PMID: 33678976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch X, Poch E, Grau JM. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):62-72 - PubMed
-
- Holt SG, Moore KP. Pathogenesis and treatment of renal dysfunction in rhabdomyolysis. Intensive Care Med. 2001;27(5):803-811 - PubMed
-
- Cervellin G, Comelli I, Lippi G. Rhabdomyolysis: historical background, clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic features. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010;48(6):749-756 - PubMed
-
- Brown CV, Rhee P, Chan L, Evans K, Demetriades D, Velmahos GC. Preventing renal failure in patients with rhabdomyolysis: do bicarbonate and mannitol make a difference? J Trauma. 2004;56(6):1191-1196 - PubMed
-
- Szpirt WM. Plasmapheresis is not justified in treatment of rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure [letter]. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1997;38(5):557 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials