A dual shaping mechanism for postsynaptic ephrin-B3 as a receptor that sculpts dendrites and synapses
- PMID: 21964490
- PMCID: PMC3203317
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2931
A dual shaping mechanism for postsynaptic ephrin-B3 as a receptor that sculpts dendrites and synapses
Abstract
As the neural network becomes wired, postsynaptic signaling molecules are thought to control the growth of dendrites and synapses. However, how these molecules are coordinated to sculpt postsynaptic structures is less well understood. We find that ephrin-B3, a transmembrane ligand for Eph receptors, functions postsynaptically as a receptor to transduce reverse signals into developing dendrites of mouse hippocampal neurons. Both tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent GRB4 SH2/SH3 adaptor-mediated signals and PSD-95-discs large-zona occludens-1 (PDZ) domain-dependent signals are required for inhibition of dendrite branching, whereas only PDZ interactions are necessary for spine formation and excitatory synaptic function. PICK1 and syntenin, two PDZ domain proteins, participate with ephrin-B3 in these postsynaptic activities. PICK1 has a specific role in spine and synapse formation, and syntenin promotes both dendrite pruning and synapse formation to build postsynaptic structures that are essential for neural circuits. The study thus dissects ephrin-B reverse signaling into three distinct intracellular pathways and protein-protein interactions that mediate the maturation of postsynaptic neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
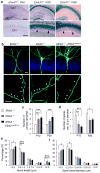

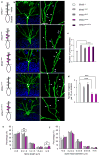

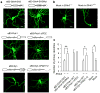
Comment in
-
EphrinBs send mixed messages.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Oct 26;14(11):1356-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.2968. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22030542 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ethell IM, Pasquale EB. Molecular mechanisms of dendritic spine development and remodeling. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;75:161–205. - PubMed
-
- Parrish JZ, Emoto K, Kim MD, Jan YN. Mechanisms that regulate establishment, maintenance, and remodeling of dendritic fields. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:399–423. - PubMed
-
- Klein R. Bidirectional modulation of synaptic functions by Eph/ephrin signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Lai KO, Ip NY. Synapse development and plasticity: roles of ephrin/Eph receptor signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2009;19:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M. Ephrins in reverse, park and drive. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:339–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

