Green tea polyphenol EGCG suppresses lung cancer cell growth through upregulating miR-210 expression caused by stabilizing HIF-1α
- PMID: 21965273
- PMCID: PMC3220612
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgr218
Green tea polyphenol EGCG suppresses lung cancer cell growth through upregulating miR-210 expression caused by stabilizing HIF-1α
Abstract
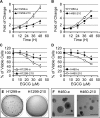
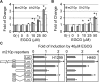
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has been reported to affect many cellular regulatory pathways. This study aims to determine whether EGCG could target microRNA (miRNA), one of the mechanisms for cells to achieve subtle change in multiple targets. We found that, in both human and mouse lung cancer cells in culture, EGCG specifically upregulated the expression of miR-210, a major miRNA regulated by HIF-1α. Furthermore, we found that overexpression of miR-210 led to reduced cell proliferation rate and anchorage-independent growth as well as reduced sensitivity to EGCG. On the mechanisms of miR-210 regulation by EGCG, we demonstrated that the regulation was mediated through the hypoxia-response element in miR-210 promoter. Consistently, the upregulation of miR-210 was found to be correlated with the stabilized HIF-1α in lung cancer cell lines after EGCG treatment. This EGCG-induced stabilization of HIF-1α was further shown by the stabilization of HA-tagged HIF-1α but not the P402A/P564A-mutated HIF-1α by EGCG, suggesting that EGCG targets the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domain. Direct evidence was obtained by affinity binding assay showing that EGCG specifically binds HIF-1α with a K(d) = 3.47 μM. This result suggests that EGCG binding interferes with the hydroxylation of key Pro residues in the ODD domain, preventing HIF-1α from the Pro hydroxylation-dependent ubiquitination and subsequent proteosome-mediated degradation. In summary, our results demonstrated, for the first time, the elevation of miR-210 by EGCG in lung cancer cell lines and this is mediated by the stabilization of HIF-1α. This event contributes to the anticancer activity of EGCG.
Figures



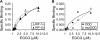
References
-
- Khan N, et al. Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2500–2505. - PubMed
-
- Liang G, et al. Green tea catechins augment the antitumor activity of doxorubicin in an in vivo mouse model for chemoresistant liver cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2010;37:111–123. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu M, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits growth and activation of the VEGF/VEGFR axis in human colorectal cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010;185:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, et al. Green tea extract and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibit hypoxia- and serum-induced HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and VEGF expression in human cervical carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1227–1238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

