Performance studies of four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography
- PMID: 21965275
- PMCID: PMC3365579
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/20/013
Performance studies of four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography
Abstract
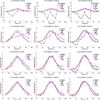
Four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography (4DCBCT) has been proposed to characterize the breathing motion of tumors before radiotherapy treatment. However, when the acquired cone beam projection data are retrospectively gated into several respiratory phases, the available data to reconstruct each phase is under-sampled and thus causes streaking artifacts in the reconstructed images. To solve the under-sampling problem and improve image quality in 4DCBCT, various methods have been developed. This paper presents performance studies of three different 4DCBCT methods based on different reconstruction algorithms. The aims of this paper are to study (1) the relationship between the accuracy of the extracted motion trajectories and the data acquisition time of a 4DCBCT scan and (2) the relationship between the accuracy of the extracted motion trajectories and the number of phase bins used to sort projection data. These aims will be applied to three different 4DCBCT methods: conventional filtered backprojection reconstruction (FBP), FBP with McKinnon-Bates correction (MB) and prior image constrained compressed sensing (PICCS) reconstruction. A hybrid phantom consisting of realistic chest anatomy and a moving elliptical object with known 3D motion trajectories was constructed by superimposing the analytical projection data of the moving object to the simulated projection data from a chest CT volume dataset. CBCT scans with gantry rotation times from 1 to 4 min were simulated, and the generated projection data were sorted into 5, 10 and 20 phase bins before different methods were used to reconstruct 4D images. The motion trajectories of the moving object were extracted using a fast free-form deformable registration algorithm. The root mean square errors (RMSE) of the extracted motion trajectories were evaluated for all simulated cases to quantitatively study the performance. The results demonstrate (1) longer acquisition times result in more accurate motion delineation for each method; (2) ten or more phase bins are necessary in 4DCBCT to ensure sufficient temporal resolution in tumor motion and (3) to achieve the same performance as FBP-4DCBCT with a 4 min data acquisition time, MB-4DCBCT and PICCS-4DCBCT need about 2- and 1 min data acquisition times, respectively.
Figures






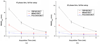
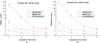
Similar articles
-
Extraction of tumor motion trajectories using PICCS-4DCBCT: a validation study.Med Phys. 2011 Oct;38(10):5530-8. doi: 10.1118/1.3637501. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21992371 Free PMC article.
-
Motion-map constrained image reconstruction (MCIR): application to four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography.Med Phys. 2013 Dec;40(12):121710. doi: 10.1118/1.4829504. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24320496
-
Faster and lower dose imaging: evaluating adaptive, constant gantry velocity and angular separation in fast low-dose 4D cone beam CT imaging.Med Phys. 2024 Feb;51(2):1364-1382. doi: 10.1002/mp.16585. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 37427751 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal structure-aware dictionary learning-based 4D CBCT reconstruction.Med Phys. 2021 Oct;48(10):6421-6436. doi: 10.1002/mp.15009. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34514608
-
Optimizing 4DCBCT projection allocation to respiratory bins.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Oct 7;59(19):5631-49. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/19/5631. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25190310
Cited by
-
Target-specific optimization of four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography.Med Phys. 2012 Sep;39(9):5683-96. doi: 10.1118/1.4747609. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22957634 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved interventional cardiac C-arm cone-beam CT: an application of the PICCS algorithm.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012 Apr;31(4):907-23. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2172951. Epub 2011 Oct 20. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22027367 Free PMC article.
-
Cine cone beam CT reconstruction using low-rank matrix factorization: algorithm and a proof-of-principle study.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014 Aug;33(8):1581-91. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2319055. Epub 2014 Apr 21. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24771574 Free PMC article.
-
Prior image constrained compressed sensing: implementation and performance evaluation.Med Phys. 2012 Jan;39(1):66-80. doi: 10.1118/1.3666946. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22225276 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of different sparsity transforms for the PICCS algorithm in small-animal respiratory gated CT.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 2;10(3):e0120140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120140. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25836670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brock KK, et al. Accuracy of finite element model-based multi-organ deformable image registration. Med. Phys. 2005;32:1647–1659. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, et al. Integrating respiratory gating into a megavoltage cone-beam CT system. Med. Phys. 2006;33:2354–2361. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich L, et al. Linac-integrated 4D cone beam CT: first experimental results. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006;51:2939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
