SCRIB expression is deregulated in human prostate cancer, and its deficiency in mice promotes prostate neoplasia
- PMID: 21965329
- PMCID: PMC3223862
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58509
SCRIB expression is deregulated in human prostate cancer, and its deficiency in mice promotes prostate neoplasia
Abstract
Loss of cellular polarity is a hallmark of epithelial cancers, raising the possibility that regulators of polarity have a role in suppressing tumorigenesis. The Scribble complex is one of at least three interacting protein complexes that have a critical role in establishing and maintaining epithelial polarity. In human colorectal, breast, and endometrial cancers, expression of the Scribble complex member SCRIB is often mislocalized and deregulated. Here, we report that Scrib is indispensable for prostate homeostasis in mice. Scrib heterozygosity initiated prostate hyperplasia, while targeted biallelic Scrib loss predisposed mice to prostate intraepithelial neoplasia. Mechanistically, Scrib was shown to negatively regulate the MAPK cascade to suppress tumorigenesis. Further analysis revealed that prostate-specific loss of Scrib in mice combined with expression of an oncogenic Kras mutation promoted the progression of prostate cancer that recapitulated the human disease. The clinical significance of the work in mice was highlighted by our observation that SCRIB deregulation strongly correlated with poor survival in human prostate cancer. These data suggest that the polarity network could provide a new avenue for therapeutic intervention.
Figures



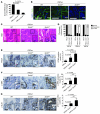
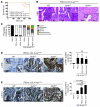

Comment in
-
Prostate cancer: Scribble complex protein deficiency promotes prostate tumors in vivo.Nat Rev Urol. 2011 Nov 15;8(12):644. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2011.167. Nat Rev Urol. 2011. PMID: 22083243 No abstract available.
-
Re: SCRIB expression is deregulated in human prostate cancer, and its deficiency in mice promotes prostate neoplasia.J Urol. 2012 Jul;188(1):324-5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.073. Epub 2012 May 17. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22682867 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

