Homozygosity mapping and exome sequencing reveal GATAD1 mutation in autosomal recessive dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 21965549
- PMCID: PMC3248690
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.111.961052
Homozygosity mapping and exome sequencing reveal GATAD1 mutation in autosomal recessive dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heritable, genetically heterogeneous disorder that typically exhibits autosomal dominant inheritance. Genomic strategies enable discovery of novel, unsuspected molecular underpinnings of familial DCM. We performed genome-wide mapping and exome sequencing in a unique family wherein DCM segregated as an autosomal recessive (AR) trait.
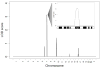
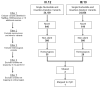
Methods and results: Echocardiography in 17 adult descendants of first cousins revealed DCM in 2 female siblings and idiopathic left ventricular enlargement in their brother. Genotyping and linkage analysis mapped an AR DCM locus to chromosome arm 7q21, which was validated and refined by high-density homozygosity mapping. Exome sequencing of the affected sisters was then used as a complementary strategy for mutation discovery. An iterative bioinformatics process was used to filter >40,000 genetic variants, revealing a single shared homozygous missense mutation localized to the 7q21 critical region. The mutation, absent in HapMap, 1000 Genomes, and 474 ethnically matched controls, altered a conserved residue of GATAD1, encoding GATA zinc finger domain-containing protein 1. Thirteen relatives were heterozygous mutation carriers with no evidence of myocardial disease, even at advanced ages. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated nuclear localization of GATAD1 in left ventricular myocytes, yet subcellular expression and nuclear morphology were aberrant in the proband.
Conclusions: Linkage analysis and exome sequencing were used as synergistic genomic strategies to identify GATAD1 as a gene for AR DCM. GATAD1 binds to a histone modification site that regulates gene expression. Consistent with murine DCM caused by genetic disruption of histone deacetylases, the data implicate an inherited basis for epigenetic dysregulation in human heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Michels VV, Moll PP, Miller FA, Tajik AJ, Chu JS, Driscoll DJ, Burnett JC, Rodeheffer RJ, Chesebro JH, Tazelaar HD. The frequency of familial dilated cardiomyopathy in a series of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Baig MK, Goldman JH, Caforio AL, Coonar AS, Keeling PJ, McKenna WJ. Familial dilated cardiomyopathy: cardiac abnormalities are common in asymptomatic relatives and may represent early disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Grünig E, Tasman JA, Kücherer H, Franz W, Kübler W, Katus HA. Frequency and phenotypes of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:186–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

