JAK/Stat signaling regulates heart precursor diversification in Drosophila
- PMID: 21965617
- PMCID: PMC3190381
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.071464
JAK/Stat signaling regulates heart precursor diversification in Drosophila
Abstract
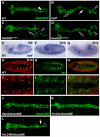
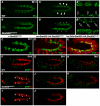
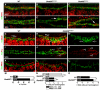
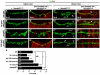
Intercellular signal transduction pathways regulate the NK-2 family of transcription factors in a conserved gene regulatory network that directs cardiogenesis in both flies and mammals. The Drosophila NK-2 protein Tinman (Tin) was recently shown to regulate Stat92E, the Janus kinase (JAK) and Signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat) pathway effector, in the developing mesoderm. To understand whether the JAK/Stat pathway also regulates cardiogenesis, we performed a systematic characterization of JAK/Stat signaling during mesoderm development. Drosophila embryos with mutations in the JAK/Stat ligand upd or in Stat92E have non-functional hearts with luminal defects and inappropriate cell aggregations. Using strong Stat92E loss-of-function alleles, we show that the JAK/Stat pathway regulates tin expression prior to heart precursor cell diversification. tin expression can be subdivided into four phases and, in Stat92E mutant embryos, the broad phase 2 expression pattern in the dorsal mesoderm does not restrict to the constrained phase 3 pattern. These embryos also have an expanded pericardial cell domain. We show the E(spl)-C gene HLHm5 is expressed in a pattern complementary to tin during phase 3 and that this expression is JAK/Stat dependent. In addition, E(spl)-C mutant embryos phenocopy the cardiac defects of Stat92E embryos. Mechanistically, JAK/Stat signals activate E(spl)-C genes to restrict Tin expression and the subsequent expression of the T-box transcription factor H15 to direct heart precursor diversification. This study is the first to characterize a role for the JAK/Stat pathway during cardiogenesis and identifies an autoregulatory circuit in which tin limits its own expression domain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GFP reporters detect the activation of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway in vivo.Gene Expr Patterns. 2007 Jan;7(3):323-31. doi: 10.1016/j.modgep.2006.08.003. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Gene Expr Patterns. 2007. PMID: 17008134
-
JAK/STAT signaling is required for hinge growth and patterning in the Drosophila wing disc.Dev Biol. 2013 Oct 15;382(2):413-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.08.016. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23978534 Free PMC article.
-
Socs36E limits STAT signaling via Cullin2 and a SOCS-box independent mechanism in the Drosophila egg chamber.Mech Dev. 2015 Nov;138 Pt 3:313-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Mech Dev. 2015. PMID: 26277564
-
Organogenesis and tumorigenesis: insight from the JAK/STAT pathway in the Drosophila eye.Dev Dyn. 2010 Oct;239(10):2522-33. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22394. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 20737505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell regulation by JAK/STAT signaling in Drosophila.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008 Aug;19(4):407-13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18603010 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of JAK-STAT pathway components: mechanisms and role in immune system development.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032777. Epub 2012 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22412924 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for tissue-specific Jak/STAT target genes in Drosophila optic lobe development.Genetics. 2013 Dec;195(4):1291-306. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.155945. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 24077308 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting pleiotropic signaling pathways to control adult cardiac stem cell fate and function.Front Physiol. 2014 Jul 1;5:219. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00219. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25071583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Iroquois complex is required in the dorsal mesoderm to ensure normal heart development in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 23;8(9):e76498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076498. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086746 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signatures of cardiac defects in Down syndrome lymphoblastoid cell lines suggest altered ciliome and Hedgehog pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041616. Epub 2012 Aug 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertet C., Rauzi M., Lecuit T. (2009). Repression of Wasp by JAK/STAT signalling inhibits medial actomyosin network assembly and apical cell constriction in intercalating epithelial cells. Development 136, 4199-4212 - PubMed
-
- Callus B. A., Mathey-Prevot B. (2002). SOCS36E, a novel Drosophila SOCS protein, suppresses JAK/STAT and EGF-R signalling in the imaginal wing disc. Oncogene 21, 4812-4821 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

