Partial inhibition of estrogen-induced mammary carcinogenesis in rats by tamoxifen: balance between oxidant stress and estrogen responsiveness
- PMID: 21966433
- PMCID: PMC3180376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025125
Partial inhibition of estrogen-induced mammary carcinogenesis in rats by tamoxifen: balance between oxidant stress and estrogen responsiveness
Abstract
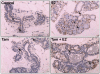
Epidemiological and experimental evidences strongly support the role of estrogens in breast tumor development. Both estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent and ER-independent mechanisms are implicated in estrogen-induced breast carcinogenesis. Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator is widely used as chemoprotectant in human breast cancer. It binds to ERs and interferes with normal binding of estrogen to ERs. In the present study, we examined the effect of long-term tamoxifen treatment in the prevention of estrogen-induced breast cancer. Female ACI rats were treated with 17β-estradiol (E2), tamoxifen or with a combination of E2 and tamoxifen for eight months. Tissue levels of oxidative stress markers 8-iso-Prostane F(2α) (8-isoPGF(2α)), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase, and oxidative DNA damage marker 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) were quantified in the mammary tissues of all the treatment groups and compared with age-matched controls. Levels of tamoxifen metabolizing enzymes cytochrome P450s as well as estrogen responsive genes were also quantified. At necropsy, breast tumors were detected in 44% of rats co-treated with tamoxifen+E2. No tumors were detected in the sham or tamoxifen only treatment groups whereas in the E2 only treatment group, the tumor incidence was 82%. Co-treatment with tamoxifen decreased GPx and catalase levels; did not completely inhibit E2-mediated oxidative DNA damage and estrogen-responsive genes monoamine oxygenase B1 (MaoB1) and cell death inducing DFF45 like effector C (Cidec) but differentially affected the levels of tamoxifen metabolizing enzymes. In summary, our studies suggest that although tamoxifen treatment inhibits estrogen-induced breast tumor development and increases the latency of tumor development, it does not completely abrogate breast tumor development in a rat model of estrogen-induced breast cancer. The inability of tamoxifen to completely inhibit E2-induced breast carcinogenesis may be because of increased estrogen-mediated oxidant burden.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




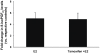




References
-
- Cavalieri E, Chakravarti D, Guttenplan J, Hart E, Ingle J, et al. Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1766:63–78. - PubMed
-
- IARC. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: hormonal contraception and postmenopausal hormone therapy. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. 1999;72:474–530.
-
- Cavalieri E, Rogan E. Catechol quinones of estrogens in the initiation of breast, prostate, and other human cancers: keynote lecture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1089:286–301. - PubMed
-
- Clemons M, Goss P. Estrogen and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:276–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

