AMPA receptor regulation at the mRNA and protein level in rat primary cortical cultures
- PMID: 21966506
- PMCID: PMC3178644
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025350
AMPA receptor regulation at the mRNA and protein level in rat primary cortical cultures
Abstract
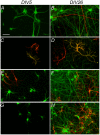
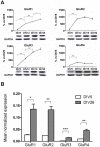
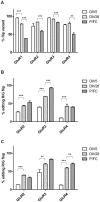
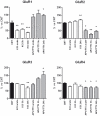
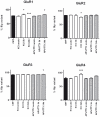
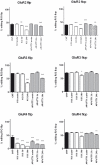
Ionotropic glutamate α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors are the major mediators of fast synaptic neurotransmission. In this work, we used primary cortical cultures from rats as a model system to study AMPA receptor regulation during in vitro cell maturation and after synaptic activity modifications. The levels of AMPA receptor mRNA and protein, along with the alternative splicing and RNA editing of the AMPA receptor subunit (GluR1-4) mRNAs, were analyzed in immature (DIV5) and mature (DIV26) rat neuronal cultures. We observed an increase in the expression of all four AMPA receptor subunits during in vitro neuronal maturation. This finding might be due to the formation of new synapses between neurons during the development of a complex neuronal network. We also analyzed the effects of stimulation (KCl and glutamate) and inhibition (APV/TTX) on rat mature neuronal cultures (DIV26): stimulation with KCl led to an overall down-regulation of GluR1 and GluR3 AMPA receptor subunits and an up-regulation of the GluR2 subunit. Similarly, glutamate treatment induced a significant down-regulation of GluR1 together with an up-regulation of GluR2. In contrast, the chronic blockade of neuronal activity that resulted from APV/TTX treatment up-regulated GluR1 and GluR3 with a parallel down-regulation of GluR2 and GluR4. RNA editing at the R/G site increased during neuronal cell maturation for all AMPA receptors (from 8-39% at DIV5 to 28-67% at DIV26). Unexpectedly, all the treatments tested induced a marked reduction (ranging from -9% to -52%) of R/G editing levels in mature neurons, primarily for the mRNA flip variant. In summary, we showed that cultured rat cortical neurons are able to vary the stoichiometric ratios of the AMPA receptor subunits and to control post-transcriptional processes to adapt fast synaptic transmission under different environmental conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in AMPA receptor-spliced variant expression and shift in AMPA receptor spontaneous desensitization pharmacology during cerebellar granule cell maturation in vitro.J Mol Neurosci. 1998 Aug;11(1):23-41. doi: 10.1385/JMN:11:1:23. J Mol Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9826784
-
mRNA expression of AMPA receptors and AMPA receptor binding proteins in the cerebral cortex of elderly schizophrenics.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Mar 15;79(6):868-78. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20423. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15696539
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates the expression and synaptic delivery of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor subunits in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 27;282(17):12619-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700607200. Epub 2007 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17337442
-
Deficient RNA editing of GluR2 and neuronal death in amyotropic lateral sclerosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Feb;83(2):110-20. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0599-z. Epub 2004 Dec 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15624111 Review.
-
The AMPAR subunit GluR2: still front and center-stage.Brain Res. 2000 Dec 15;886(1-2):190-207. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02951-6. Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11119696 Review.
Cited by
-
GluA2 is rapidly edited at the Q/R site during neural differentiation in vitro.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar 5;9:69. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00069. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25798088 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Oct;73(4):298-487. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000131. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of dendritic AMPA receptor mRNA trafficking by RNA splicing and editing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan 7;41(1):617-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1223. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23166306 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA Receptors Are Involved in Store-Operated Calcium Entry and Interact with STIM Proteins in Rat Primary Cortical Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Oct 25;10:251. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00251. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27826230 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR RNA editing in human disease; more to it than meets the I.Hum Genet. 2017 Sep;136(9):1265-1278. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1837-0. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28913566 Review.
References
-
- Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
-
- Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Huber KM, Warren ST. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:370–377. - PubMed
-
- Marenco S, Weinberger DR. Therapeutic potential of positive AMPA receptor modulators in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Drugs. 2006;20:173–185. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill MJ, Bleakman D, Zimmerman DM, Nisenbaum ES. AMPA receptor potentiators for the treatment of CNS disorders. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004;3:181–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

