Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders
- PMID: 21967517
- PMCID: PMC3212803
- DOI: 10.1515/RNS.2011.044
Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders
Abstract
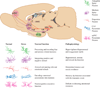
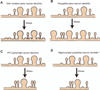
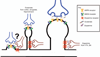
Abstract Stress can have a lasting impact on the structure and function of brain circuitry that results in long-lasting changes in the behavior of an organism. Synaptic plasticity is the mechanism by which information is stored and maintained within individual synapses, neurons, and neuronal circuits to guide the behavior of an organism. Although these mechanisms allow the organism to adapt to its constantly evolving environment, not all of these adaptations are beneficial. Under prolonged bouts of physical or psychological stress, these mechanisms become dysregulated, and the connectivity between brain regions becomes unbalanced, resulting in pathological behaviors. In this review, we highlight the effects of stress on the structure and function of neurons within the mesocorticolimbic brain systems known to regulate mood and motivation. We then discuss the implications of these spine adaptations on neuronal activity and pathological behaviors implicated in mood disorders. Finally, we end by discussing recent brain imaging studies in human depression within the context of these basic findings to provide insight into the underlying mechanisms leading to neural dysfunction in depression.
Figures
References
-
- Akram A, Christoffel D, Rocher AB, Bouras C, Kövari E, Perl DP, Morrison JH, Herrmann FR, Haroutunian V, Giannakopoulos P, et al. Stereologic estimates of total spinophilin-immunoreactive spine number in area 9 and the CA1 field: relationship with the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2008;29:1296–1307. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennur S, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Pawlak R, Strickland S, McEwen BS, Chattarji S. Stress-induced spine loss in the medial amygdala is mediated by tissue-plasminogen activator. Neuroscience. 2007;144:8–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
