Galanin negatively modulates opiate withdrawal via galanin receptor 1
- PMID: 21969124
- PMCID: PMC3324978
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2515-x
Galanin negatively modulates opiate withdrawal via galanin receptor 1
Abstract
Rationale: The neuropeptide galanin has been shown to modulate opiate dependence and withdrawal. These effects could be mediated via activation of one or more of the three distinct G protein-coupled receptors, namely galanin receptors 1 (GalR1), 2 (GalR2), and 3 (GalR3).
Objectives: In this study, we used several transgenic mouse lines to further define the mechanisms underlying the role played by galanin and its receptors in the modulation of morphine dependence. First, transgenic mice expressing β-galactosidase under the control of the galanin promoter were used to assess the regulation of galanin expression in response to chronic morphine administration and withdrawal. Next, the behavioral responses to chronic morphine administration and withdrawal were tested in mice that over-express galanin, lack the GalR1 gene, or lack the GalR2 gene.
Methods: Transgenic and matched wild-type mice were given increasing doses of morphine followed by precipitation of withdrawal by naloxone and behavioral responses to withdrawal were assessed.
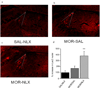
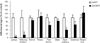
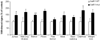
Results: Both morphine administration and withdrawal increased galanin gene transcription in the locus coeruleus (LC). Increasing galanin levels in the brain reduced signs of opiate withdrawal. Mice lacking GalR1 undergo more severe opiate withdrawal, whereas mice lacking GalR2 show no significant difference in withdrawal signs, compare with matched wild-type controls.
Conclusions: Opiate administration and withdrawal increase galanin expression in the LC. Galanin opposes the actions of morphine which leads to opiate dependence and withdrawal, an effect that is mediated via GalR1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of GalR1, GalR2, and GalR3 immunoreactivity in catecholaminergic nuclei of the mouse brain.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Nov 22;479(4):410-23. doi: 10.1002/cne.20329. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15514977
-
GalR1, but not GalR2 or GalR3, levels are regulated by galanin signaling in the locus coeruleus through a cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism.J Neurochem. 2005 Jun;93(5):1168-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03105.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15934937 Free PMC article.
-
Galanin-induced decreases in nucleus accumbens/striatum excitatory postsynaptic potentials and morphine conditioned place preference require both galanin receptor 1 and galanin receptor 2.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 May;37(9):1541-9. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12151. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23387435 Free PMC article.
-
Galanin can attenuate opiate reinforcement and withdrawal.Neuropeptides. 2005 Jun;39(3):313-5. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2004.12.001. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Neuropeptides. 2005. PMID: 15944028 Review.
-
Palmitate differentially regulates Spexin, and its receptors Galr2 and Galr3, in GnRH neurons through mechanisms involving PKC, MAPKs, and TLR4.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 1;518:110991. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110991. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32841709 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of neurological and neuropsychiatric phenotypes by locus coeruleus-derived galanin.Brain Res. 2016 Jun 15;1641(Pt B):320-37. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.025. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26607256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Spexin-based Human Galanin Receptor Type II-Specific Agonists with Increased Stability in Serum and Anxiolytic Effect in Mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 24;6:21453. doi: 10.1038/srep21453. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26907960 Free PMC article.
-
A high-fat diet or galanin in the PVN decreases phosphorylation of CREB in the nucleus accumbens.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 17;248:61-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.046. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23747305 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type specific expression and behavioral impact of galanin and GalR1 in the locus coeruleus during opioid withdrawal.Addict Biol. 2021 Sep;26(5):e13037. doi: 10.1111/adb.13037. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Addict Biol. 2021. PMID: 33768673 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal diversity of neuropeptide signaling, including galanin, in the mouse locus coeruleus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug;120(31):e2222095120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2222095120. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37487094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Branchek TA, Smith KE, Gerald C, Walker MW. Galanin receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2000;21:109–117. - PubMed
-
- Burgevin MC, Loquet I, Quarteronet D, Habert-Ortoli E. Cloning, pharmacological characterization, and anatomical distribution of a rat cDNA encoding for a galanin receptor. J Mol Neurosci. 1995;6:33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

