Expression and functional roles of caspase-5 in inflammatory responses of human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- PMID: 21969293
- PMCID: PMC3230287
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.11-7570
Expression and functional roles of caspase-5 in inflammatory responses of human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the expression, activation, and functional involvement of caspase-5 in human retinal pigment epithelial (hRPE) cells.
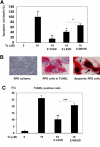
Methods: Expression and activation of caspase-5 in primary cultured hRPE cells, telomerase-immortalized hTERT-RPE1 cells (hTERT-RPE1), or both, were measured after stimulation with proinflammatory agents IL-1β, TNF-α, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), interferon-γ, monocyte coculture, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducers. Immunomodulating agents dexamethasone (Dex), IL-10, and triamcinolone acetonide (TA) were used to antagonize proinflammatory stimulation. Cell death ELISA and TUNEL staining assays were used to assess apoptosis.
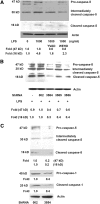
Results: Caspase-5 mRNA expression and protein activation were induced by LPS and monocyte-hRPE coculture. Caspase-5 activation appeared as early as 2 hours after challenge by LPS and consistently increased to 24 hours. Meanwhile, caspase-1 expression and protein activation were induced by LPS. Activation of caspase-5 was blocked or reduced by Dex, IL-10, and TA. Activation of caspase-5 and -1 was also enhanced by ATP and ER stress inducers. Expression and activation of caspase-5 were inhibited by a caspase-1-specific inhibitor. Caspase-5 knockdown reduced caspase-1 protein expression and activation and inhibited TNF-α-induced IL-8 and MCP-1. In contrast to caspase-4, the contribution of caspase-5 to stress-induced apoptosis was moderate.
Conclusions: Caspase-5 mRNA synthesis, protein expression, and catalytic activation were highly regulated in response to various proinflammatory stimuli, ATP, and ER stress inducers. Mutual activation between caspase-5 and -1 suggests caspase-5 may work predominantly in concert with caspase-1 in modulating hRPE inflammatory responses.
Figures





References
-
- Munday NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ali A, et al. Molecular cloning and pro-apoptotic activity of ICErelII and ICErelIII, members of the ICE/CED-3 family of cysteine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:15870–15876 - PubMed
-
- Faucheu C, Blanchet AM, Collard-Dutilleul V, Lalanne JL, Diu-Hercend A. Identification of a cysteine protease closely related to interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1996;236:207–213 - PubMed
-
- Lin XY, Choi MS, Porter AG. Expression analysis of the human caspase-1 subfamily reveals specific regulation of the CASP5 gene by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39920–39926 - PubMed
-
- Eckhart L, Kittel C, Gawlas S, et al. Identification of a novel exon encoding the amino-terminus of the predominant caspase-5 variants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;348:682–688 - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Tschopp J. Inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes: master switches of inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:10–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

