Cisplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 30306, a phase II study
- PMID: 21969504
- PMCID: PMC3221525
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.6923
Cisplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 30306, a phase II study
Abstract
Purpose: The efficacy of cisplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab was evaluated in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
Patients and methods: Patients with ES-SCLC received cisplatin 30 mg/m(2) and irinotecan 65 mg/m(2) on days 1 and 8 plus bevacizumab 15 mg/kg on day 1 every 21 days for six cycles on this phase II study. The primary end point was to differentiate between 50% and 65% 12-month survival rates.
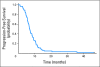
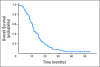
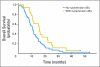
Results: Seventy-two patients were enrolled between March 2005 and April 2006; four patients canceled, and four were ineligible. Grade 3 or 4 toxicities included neutropenia (25%), all electrolyte (23%), diarrhea (16%), thrombocytopenia (10%), fatigue (10%), nausea (10%), hypertension (9%), anemia (9%), infection (7%), vascular access thrombosis (2%), stroke (2%), and bowel perforation (1%). Three deaths (5%) occurred on therapy as a result of pneumonitis (n = 1), stroke (n =1), and heart failure (n = 1). Complete response, partial response, and stable disease occurred in three (5%), 45 (70%), and 11 patients (17%), respectively. Progressive disease occurred in one patient (2%). Overall response rate was 75%. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 7.0 months (95% CI, 6.4 to 8.4 months). Median overall survival (OS) was 11.6 months (95% CI, 10.5 to 15.1 months). Hypertension ≥ grade 1 was associated with improved OS after adjusting for performance status (PS) and age (hazard ratio [HR], 0.55; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.97; P = .04). Lower vascular endothelial growth factor levels correlated with worse PFS after adjusting for age and PS (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.83 to 0.99; P = .03).
Conclusion: PFS and OS times were higher compared with US trials in ES-SCLC with the same chemotherapy. However, the primary end point of the trial was not met. Hypertension was associated with improved survival after adjusting for age and PS.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 10;27(35):6006-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7545. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19826110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combination chemotherapy with irinotecan and cisplatin in elderly patients (>or= 65 years) with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2008 Aug;61(2):220-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.12.020. Epub 2008 Feb 12. Lung Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18272249 Clinical Trial.
-
Etoposide and cisplatin versus irinotecan and cisplatin in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with etoposide and cisplatin plus concurrent accelerated hyperfractionated thoracic radiotherapy (JCOG0202): a randomised phase 3 study.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Jan;15(1):106-13. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70511-4. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24309370 Clinical Trial.
-
Irinotecan plus cisplatin in small-cell lung cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 2002 Sep;16(9 Suppl 9):39-43. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002. PMID: 12375800 Review.
-
Camptothecin and Its Derivatives from Traditional Chinese Medicine in Combination with Anticancer Therapy Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 12;16(22):3802. doi: 10.3390/cancers16223802. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39594757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A phase II study of anlotinib in 45 patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer.Int J Cancer. 2020 Dec 15;147(12):3453-3460. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33161. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32557583 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment options for small cell lung cancer - do we have more choice?Br J Cancer. 2010 Feb 16;102(4):629-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605527. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20104223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase II study of Cediranib (AZD 2171), an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, for second-line therapy of small cell lung cancer (National Cancer Institute #7097).J Thorac Oncol. 2010 Aug;5(8):1279-84. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e2fcb0. J Thorac Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20559150 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized phase 2 trial of apatinib vs observation as maintenance treatment following first-line induction chemotherapy in extensive- stage small cell lung cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Feb;38(1):148-159. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00828-x. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31399906 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 10;27(35):6006-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7545. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19826110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Travis WD, Travis LB, Percy C, et al. Lung cancer incidence and survival by histologic type. Cancer. 1995;75:191–202. - PubMed
-
- Miller AA, Herndon J, Hollis DR, et al. Schedule dependency of 21-day oral versus 3-day intravenous etoposide in combination with intravenous cisplatin in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: A randomized phase III study of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1871–1879. - PubMed
-
- Chute JP, Chen T, Feigal E, et al. Twenty years of phase III trials for patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Perceptible progress. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1794–1801. - PubMed
-
- Niell HB, Herndon JE, 2nd, Miller AA, et al. Randomized phase III intergroup trial of etoposide and cisplatin with or without paclitaxel and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 9732. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3752–3759. - PubMed
-
- Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:85–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous