Acquired Pure Red Cell Aplasia caused by Parvovirus B19 Infection following a Renal Transplant
- PMID: 21969904
- PMCID: PMC3121037
Acquired Pure Red Cell Aplasia caused by Parvovirus B19 Infection following a Renal Transplant
Abstract
We report a young Omani male who developed severe and persistent anaemia after a kidney transplantation while being on immunosuppression therapy, standard practice to prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney. His bone marrow aspirate showed the classic morphological changes of pure red cell aplasia (PRCA), induced by parvovirus B19 infection which is the presence of giant proerythroblasts with viral inclusions. The virus was also demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction in the blood along with IgM antibodies to parvovirus B19. He responded dramatically to high dose immunoglobulin with a normalisation of his haemoglobin level in two weeks and remained normal until seven months later. Parvovirus B19 induced PRCA can be cured. This aetiology must be kept in mind especially when a chronic anaemia, refractory to treatment, is accompanied by a reticulocytopenia. The latter reflects the lysis of the proerythroblasts, preventing maturation of the erythroid cells causing anaemia. Early recognition and prompt treatment spares the patient unnecessary exposure to blood transfusions, erythropoietin and renal disease caused by the virus. PRCA secondary to parvovirus B19 infection following kidney transplantation is reported in the literature, but not in the Omani population. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first such report in Oman.
Keywords: Case report; Immunosuppuression; Oman; Red cell aplasia, pure; human parvovirus B19; kidney transplantation.
Figures
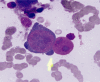

References
-
- Brown KE, Anderson SM, Young NS. Erythrocyte P antigen: Cellular receptor for B10 parvo virus. Science. 1993;262:114–17. - PubMed
-
- Forea AV, Lonescu DN, Melhem MF. Parvovirus B19 infection in the immunocompromised host. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:799–804. - PubMed
-
- Hayes-Lattin B, Seipei J, Gatter K, Heinrich MC, Mariarz T. Pure red cell aplasia associated with parvovirus B19 infection occurring late after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. American J Hematol. 2004;75:142–5. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Maruta A, Yamamoto T, Katayama N, Higuichi R, Sakano Y, et al. Human parvovirus B19 capsid antigen in granulocytes in parvovirus B19 induced pancytopenia after bone marrow transplantation. Acta Haematol. 1998;100:195–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
