The Escherichia coli clamp loader can actively pry open the β-sliding clamp
- PMID: 21971175
- PMCID: PMC3234947
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.268169
The Escherichia coli clamp loader can actively pry open the β-sliding clamp
Abstract
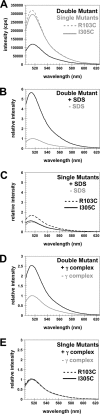
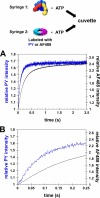
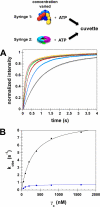
Clamp loaders load ring-shaped sliding clamps onto DNA. Once loaded onto DNA, sliding clamps bind to DNA polymerases to increase the processivity of DNA synthesis. To load clamps onto DNA, an open clamp loader-clamp complex must form. An unresolved question is whether clamp loaders capture clamps that have transiently opened or whether clamp loaders bind closed clamps and actively open clamps. A simple fluorescence-based clamp opening assay was developed to address this question and to determine how ATP binding contributes to clamp opening. A direct comparison of real time binding and opening reactions revealed that the Escherichia coli γ complex binds β first and then opens the clamp. Mutation of conserved "arginine fingers" in the γ complex that interact with bound ATP decreased clamp opening activity showing that arginine fingers make an important contribution to the ATP-induced conformational changes that allow the clamp loader to pry open the clamp.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mechanism of opening a sliding clamp.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 29;45(17):10178-10189. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx665. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28973453 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of an "open" E. coli Pol III clamp loader sliding clamp complex.J Struct Biol. 2016 Jun;194(3):272-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 26968362
-
Dynamics of loading the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase processivity clamp.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 May-Jun;41(3):179-208. doi: 10.1080/10409230600648751. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16760017 Review.
-
A function for the psi subunit in loading the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase sliding clamp.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7035-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610136200. Epub 2007 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17210572
-
Replication clamps and clamp loaders.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Apr 1;5(4):a010165. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010165. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23545418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the large terminase from a hyperthermophilic virus reveals a unique mechanism for oligomerization and ATP hydrolysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Dec 15;45(22):13029-13042. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx947. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29069443 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic Interactions at the Dimer Interface Stabilize the E. coli β Sliding Clamp.Biophys J. 2017 Aug 22;113(4):794-804. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.06.057. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28834716 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between bacteria and eukaryotes in clamp loader mechanism, a conserved process underlying DNA replication.J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):107166. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107166. Epub 2024 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38490435 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in clamp loader mechanism between bacteria and eukaryotes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 30:2023.11.30.569468. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.30.569468. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):107166. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107166. PMID: 38076975 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The β sliding clamp closes around DNA prior to release by the Escherichia coli clamp loader γ complex.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 11;288(2):1162-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.406231. Epub 2012 Nov 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23161545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gulbis J. M., Kelman Z., Hurwitz J., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. (1996) Cell 87, 297–306 - PubMed
-
- Kong X. P., Onrust R., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. (1992) Cell 69, 425–437 - PubMed
-
- Moarefi I., Jeruzalmi D., Turner J., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. (2000) J. Mol. Biol. 296, 1215–1223 - PubMed
-
- Shamoo Y., Steitz T. A. (1999) Cell 99, 155–166 - PubMed
-
- Leu F. P., Hingorani M. M., Turner J., O'Donnell M. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 34609–34618 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

