BSP-SLIM: a blind low-resolution ligand-protein docking approach using predicted protein structures
- PMID: 21971880
- PMCID: PMC3240723
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.23165
BSP-SLIM: a blind low-resolution ligand-protein docking approach using predicted protein structures
Abstract
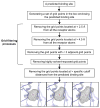
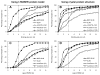
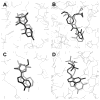
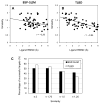
We developed BSP-SLIM, a new method for ligand-protein blind docking using low-resolution protein structures. For a given sequence, protein structures are first predicted by I-TASSER; putative ligand binding sites are transferred from holo-template structures which are analogous to the I-TASSER models; ligand-protein docking conformations are then constructed by shape and chemical match of ligand with the negative image of binding pockets. BSP-SLIM was tested on 71 ligand-protein complexes from the Astex diverse set where the protein structures were predicted by I-TASSER with an average RMSD 2.92 Å on the binding residues. Using I-TASSER models, the median ligand RMSD of BSP-SLIM docking is 3.99 Å which is 5.94 Å lower than that by AutoDock; the median binding-site error by BSP-SLIM is 1.77 Å which is 6.23 Å lower than that by AutoDock and 3.43 Å lower than that by LIGSITE(CSC) . Compared to the models using crystal protein structures, the median ligand RMSD by BSP-SLIM using I-TASSER models increases by 0.87 Å, while that by AutoDock increases by 8.41 Å; the median binding-site error by BSP-SLIM increase by 0.69Å while that by AutoDock and LIGSITE(CSC) increases by 7.31 Å and 1.41 Å, respectively. As case studies, BSP-SLIM was used in virtual screening for six target proteins, which prioritized actives of 25% and 50% in the top 9.2% and 17% of the library on average, respectively. These results demonstrate the usefulness of the template-based coarse-grained algorithms in the low-resolution ligand-protein docking and drug-screening. An on-line BSP-SLIM server is freely available at http://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/BSP-SLIM.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Nonlinear scoring functions for similarity-based ligand docking and binding affinity prediction.J Chem Inf Model. 2013 Nov 25;53(11):3097-112. doi: 10.1021/ci400510e. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Chem Inf Model. 2013. PMID: 24171431
-
EDock: blind protein-ligand docking by replica-exchange monte carlo simulation.J Cheminform. 2020 May 27;12(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13321-020-00440-9. J Cheminform. 2020. PMID: 33430966 Free PMC article.
-
I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W174-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv342. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25883148 Free PMC article.
-
Docking and scoring with ICM: the benchmarking results and strategies for improvement.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012 Jun;26(6):675-86. doi: 10.1007/s10822-012-9547-0. Epub 2012 May 9. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012. PMID: 22569591 Free PMC article.
-
Are predicted protein structures of any value for binding site prediction and virtual ligand screening?Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Apr;23(2):191-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23415854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GPCR-I-TASSER: A Hybrid Approach to G Protein-Coupled Receptor Structure Modeling and the Application to the Human Genome.Structure. 2015 Aug 4;23(8):1538-1549. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Structure. 2015. PMID: 26190572 Free PMC article.
-
FINDSITE(X): a structure-based, small molecule virtual screening approach with application to all identified human GPCRs.Mol Pharm. 2012 Jun 4;9(6):1775-84. doi: 10.1021/mp3000716. Epub 2012 May 21. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22574683 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning assessment of the binding region as a tool for more efficient computational receptor-ligand docking.J Mol Liq. 2022 May 1;353:118759. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118759. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Mol Liq. 2022. PMID: 35273421 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand binding site detection by local structure alignment and its performance complementarity.J Chem Inf Model. 2013 Sep 23;53(9):2462-70. doi: 10.1021/ci4003602. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Chem Inf Model. 2013. PMID: 23957286 Free PMC article.
-
Fast docking on graphics processing units via Ray-Casting.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 16;8(8):e70661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070661. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23976948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taft CA, Da Silva VB, Da Silva CH. Current topics in computer-aided drug design. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97:1089–1098. - PubMed
-
- Koppen H. Virtual screening - what does it give us? Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2009;12:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Sousa SF, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ. Protein-ligand docking: current status and future challenges. Proteins. 2006;65:15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

