Structural definition of trehalose 6-monomycolates and trehalose 6,6'-dimycolates from the pathogen Rhodococcus equi by multiple-stage linear ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization
- PMID: 21972013
- PMCID: PMC3938585
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-011-0240-7
Structural definition of trehalose 6-monomycolates and trehalose 6,6'-dimycolates from the pathogen Rhodococcus equi by multiple-stage linear ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization
Abstract
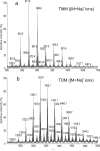
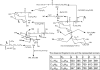
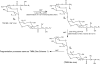
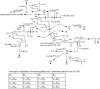
The cell wall of the pathogenic bacterium Rhodococcus equi (R. equi) contains abundant trehalose monomycolate (TMM) and trehalose dimycolate (TDM), the glycolipids bearing mycolic acids. Here, we describe multiple-stage (MS(n)) linear ion-trap (LIT) mass spectrometric approaches toward structural characterization of TMM and TDM desorbed as [M + Alk](+) (Alk = Na, Li) and as [M + X](-) (X = CH(3)CO(2), HCO(2)) ions by electrospray ionization (ESI). Upon MS(n) (n=2, 3, 4) on the [M + Alk](+) or the [M + X](-) adduct ions of TMM and TDM, abundant structurally informative fragment ions are readily available, permitting fast assignment of the length of the meromycolate chain and of the α-branch on the mycolyl residues. In this way, structures of TMM and TDM isolated from pathogenic R. equi strain 103 can be determined. Our results indicate that the major TMM and TDM molecules possess 6, and/or 6'-mycolyl groups that consist of mainly C14 and C16 α-branches with meromycolate branches ranging from C18 to C28, similar to the structures of the unbound mycolic acids found in the cell envelope. Up to 60 isobaric isomers varying in chain length of the α-branch and of the meromycolate backbone were observed for some of the TDM species in the mixture. This mass spectrometric approach provides a direct method that affords identification of various TMM and TDM isomers in a mixture of which the complexity of this lipid class has not been previously reported using other analytical methods.
© American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2011
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of mycolic acids from the pathogen Rhodococcus equi by tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization.Anal Biochem. 2011 Feb 1;409(1):112-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Anal Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20946862 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationship of mycoloyl glycolipids derived from Rhodococcus sp. 4306.Microb Pathog. 2001 Feb;30(2):91-9. doi: 10.1006/mpat.2000.0413. Microb Pathog. 2001. PMID: 11162189
-
Structural Determination of a New Peptidolipid Family from Rhodococcus opacus and the Pathogen Rhodococcus equi by Multiple Stage Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020 Mar 4;31(3):611-623. doi: 10.1021/jasms.9b00059. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 31967470
-
Genetic Susceptibility to Rhodococcus equi.J Vet Intern Med. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(6):1648-59. doi: 10.1111/jvim.13616. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Vet Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26340305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogenic actinobacterium Rhodococcus equi: what's in a name?Mol Microbiol. 2019 Jul;112(1):1-15. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14267. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31099908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a Bacterial Lipidomics Analytical Platform: Pilot Validation with Bovine Paratuberculosis Serum.Metabolites. 2023 Jun 29;13(7):809. doi: 10.3390/metabo13070809. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37512516 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determination of glycopeptidolipids of Mycobacterium smegmatis by high-resolution multiple-stage linear ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization.J Mass Spectrom. 2012 Oct;47(10):1269-81. doi: 10.1002/jms.3070. J Mass Spectrom. 2012. PMID: 23019158 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of mass spectrometry for cellular lipid analysis.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Mar;11(3):698-713. doi: 10.1039/c4mb00586d. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 25598407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversion of phagosome trafficking by pathogenic Rhodococcus equi depends on mycolic acid chain length.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Mar;15(3):458-73. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12050. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23078612 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the virulence-associated protein VapD from the intracellular pathogen Rhodococcus equi.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Aug;70(Pt 8):2139-51. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714012632. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25084333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giguère S, Prescott JF. Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Rhodococcus Equi Infections in Foals. Vet. Microbiol. 1997;56:313–334. - PubMed
-
- von Bargen K, Haas A. Molecular and Infection Biology of the Horse Pathogen Rhodococcus Equi. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33:870–891. - PubMed
-
- Sutcliffe IC. Cell Envelope Composition and Organisation in the Genus Rhodococcus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 1998;74:49–58. - PubMed
-
- Sutcliffe I, Brown A, Dover L. The Rhodococcal Cell Envelope: Composition, Organisation and Biosynthesis. Journal. 2010;16:29–71.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01-HL-57278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK034388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103422/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK-34388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027197/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR-00954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60-DK-20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

