Functionalization of reactive polymer multilayers with RGD and an antifouling motif: RGD density provides control over human corneal epithelial cell-substrate interactions
- PMID: 21972074
- PMCID: PMC3222791
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.33233
Functionalization of reactive polymer multilayers with RGD and an antifouling motif: RGD density provides control over human corneal epithelial cell-substrate interactions
Abstract
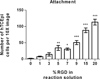
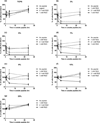
Our study demonstrates that substrates fabricated using a "reactive" layer-by-layer approach promote well-defined cell-substrate interactions of human corneal epithelial cells. Specifically, crosslinked and amine-reactive polymer multilayers were produced by alternating "reactive" deposition of an azlactone-functionalized polymer [poly(2-vinyl-4,4-dimethylazlactone)] (PVDMA) and a primary amine-containing polymer [branched poly(ethylene imine)] (PEI). Advantages of our system include a 5- to 30-fold decrease in deposition time compared to traditional polyelectrolyte films and direct modification of the films with peptides. Our films react with mixtures of an adhesion-promoting peptide containing Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) and the small molecule D-glucamine, a chemical motif which is nonfouling. Resulting surfaces prevent protein adsorption and promote cell attachment through specific peptide interactions. The specificity of cell attachment via immobilized RGD sequences was verified using both a scrambled RDG peptide control as well as soluble-RGD competitive assays. Films were functionalized with monotonically increasing surface densities of RGD which resulted in both increased cell attachment and the promotion of a tri-phasic proliferative response of a human corneal epithelial cell line (hTCEpi). The ability to treat PEI/PVDMA films with peptides for controlled cell-substrate interactions enables the use of these films in a wide range of biological applications.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The influence of biomimetic topographical features and the extracellular matrix peptide RGD on human corneal epithelial contact guidance.Acta Biomater. 2013 Feb;9(2):5040-51. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23069317 Free PMC article.
-
Free-standing and reactive thin films fabricated by covalent layer-by-layer assembly and subsequent lift-off of azlactone-containing polymer multilayers.Langmuir. 2010 Oct 19;26(20):16134-40. doi: 10.1021/la103009a. Langmuir. 2010. PMID: 20857952 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable Amine-Reactive Coatings Fabricated by the Covalent Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Poly(2-vinyl-4,4-dimethylazlactone) with Degradable Polyamine Building Blocks.Biomacromolecules. 2016 Sep 12;17(9):3067-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00975. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Biomacromolecules. 2016. PMID: 27525718
-
Fabrication and selective functionalization of amine-reactive polymer multilayers on topographically patterned microwell cell culture arrays.Biomacromolecules. 2011 Jun 13;12(6):1998-2007. doi: 10.1021/bm200296a. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Biomacromolecules. 2011. PMID: 21504222 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical modification of reactive multilayered films fabricated from poly(2-alkenyl azlactone)s: design of surfaces that prevent or promote mammalian cell adhesion and bacterial biofilm growth.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Jun 8;10(6):1564-74. doi: 10.1021/bm9001552. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19438231 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic stochastic topography and electric fields synergistically enhance directional migration of corneal epithelial cells in a MMP-3-dependent manner.Acta Biomater. 2015 Jan;12:102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.10.007. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25311684 Free PMC article.
-
Isotopic tracing for calculating the surface density of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-containing peptide on allogeneic bone.Orthop Surg. 2013 Feb;5(1):51-5. doi: 10.1111/os.12029. Orthop Surg. 2013. PMID: 23420748 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive polymer multilayers fabricated by covalent layer-by-layer assembly: 1,4-conjugate addition-based approaches to the design of functional biointerfaces.Biomacromolecules. 2012 May 14;13(5):1523-32. doi: 10.1021/bm300234q. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Biomacromolecules. 2012. PMID: 22468967 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of YAP, TAZ and HSP90 in contact guidance and intercellular junction formation in corneal epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 7;9(10):e109811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109811. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25290150 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of biomimetic topographical features and the extracellular matrix peptide RGD on human corneal epithelial contact guidance.Acta Biomater. 2013 Feb;9(2):5040-51. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23069317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984;309(5963):30–33. - PubMed
-
- Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987;238(4826):491–497. - PubMed
-
- Rowley JA, Mooney DJ. Alginate type and RGD density control myoblast phenotype. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. 2002;60(2):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Harbers GM, Healy KE. The effect of ligand type and density on osteoblast adhesion, proliferation, and matrix mineralization. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 2005;75(4):855–869. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Ma L, Yang S, Shao Z, Meng C, Duan D, Li Y. Effect of RGD-modified silk material on the adhesion and proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical sciences. 2009;29(1):80–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

