The efficacy and safety of valsartan in obese and non-obese pediatric hypertensive patients
- PMID: 21974764
- PMCID: PMC8108891
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00502.x
The efficacy and safety of valsartan in obese and non-obese pediatric hypertensive patients
Abstract
This post hoc analysis assessed the efficacy and tolerability of valsartan for the treatment of hypertension in obese vs non-obese children and adolescents. After a 1-week antihypertensive washout period, 142 obese and 119 non-obese hypertensive children and adolescents aged 6 to 16 years were randomized to 2 weeks of once-daily treatment with valsartan 10 to 20 mg, 40 to 80 mg, or 80 to 160 mg, followed by re-randomization to either valsartan or placebo for an additional 2 weeks. Patients could continue to receive valsartan during an optional 52-week, open-label extension. Valsartan resulted in statistically significant (P<.05) and clinically relevant reductions in mean sitting blood pressure (BP), ranging from approximately 7/4 mm Hg (valsartan 10-20 mg) to 13/9 mm Hg (valsartan 80-160 mg) in both obese and non-obese patients. BP control was achieved in 44% of obese and 56% of non-obese patients. Following re-randomization, non-obese patients experienced an increase in BP during placebo treatment, albeit levels remained below baseline, whereas BP reductions were maintained in valsartan recipients (P<.05). The most frequent adverse events during the open-label phase were headache and fever. Valsartan provides similar antihypertensive efficacy in obese and non-obese hypertensive children and adolescents, with good tolerability in both patient populations.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
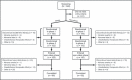
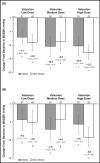
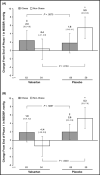
References
-
- Markham A, Goa KL. Valsartan. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in essential hypertension. Drugs. 1997;54:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Wagstaff AJ. Valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs. 2006;66:1881–1901. - PubMed
-
- Plosker GL, Robinson DM. Amlodipine/valsartan: fixed‐dose combination in hypertension. Drugs. 2008;68:373–381. - PubMed
-
- Cohn JN, Tognoni G. A randomized trial of the angiotensin‐receptor blocker valsartan in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1667–1675. - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ, et al. Valsartan, captopril, or both in myocardial infarction complicated by heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or both. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1893–1906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

