Assessing intern core competencies with an objective structured clinical examination
- PMID: 21975704
- PMCID: PMC2931201
- DOI: 10.4300/01.01.0006
Assessing intern core competencies with an objective structured clinical examination
Abstract
Background: Residents are evaluated using Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) core competencies. An Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) is a potential evaluation tool to measure these competencies and provide outcome data.
Objective: Create an OSCE to evaluate and demonstrate improvement in intern core competencies of patient care, medical knowledge, practice-based learning and improvement, interpersonal and communication skills, professionalism, and systems-based practice before and after internship.
Methods: From 2006 to 2008, 106 interns from 10 medical specialties were evaluated with a preinternship and postinternship OSCE at Madigan Army Medical Center. The OSCE included eight 12-minute stations that collectively evaluated the 6 ACGME core competencies using human patient simulators, standardized patients, and clinical scenarios. Interns were scored using objective and subjective criteria, with a maximum score of 100 for each competency. Stations included death notification, abdominal pain, transfusion consent, suture skills, wellness history, chest pain, altered mental status, and computer literature search. These stations were chosen by specialty program directors, created with input from board-certified specialists, and were peer reviewed.
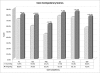
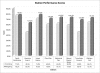
Results: All OSCE testing on the 106 interns (ages 25 to 44 [average, 28.6]; 70 [66%] men; 65 [58%] allopathic medical school graduates) resulted in statistically significant improvement in all ACGME core competencies: patient care (71.9% to 80.0%, P < .001), medical knowledge (59.6% to 78.6%, P < .001), practice-based learning and improvement (45.2% to 63.0%, P < .001), interpersonal and communication skills (77.5% to 83.1%, P < .001), professionalism (74.8% to 85.1%, P < .001), and systems-based practice (56.6% to 76.5%, P < .001).
Conclusion: An OSCE during internship can evaluate incoming baseline ACGME core competencies and test for interval improvement. The OSCE is a valuable assessment tool to provide outcome measures on resident competency performance and evaluate program effectiveness.
Figures
References
-
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Outcome project. Available at: http://www.acgme.org/Outcome/. Accessed April 16, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education and American Board of Medical Specialties Joint Initiative. Toolbox of assessment methods. Version 1.0, Summer 2000. Available at: http://www.acgme.org/Outcome/assess/Toolbox.pdf. Accessed April 16, 2009.
-
- Casey P. M., Goepfert A. R., Espey E. L. To the point: reviews in medical education–the Objective Structured Clinical Examination. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200(1):25–34. - PubMed
-
- Simon S. R., Bui A., Day S., Berti D., Volkan K. The relationship between second-year medical students' OSCE scores and USMLE Step 2 scores. J Eval Clin Pract. 2007;13(6):901–905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources