Fluoroquinolones for treating typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever)
- PMID: 21975746
- PMCID: PMC6532575
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004530.pub4
Fluoroquinolones for treating typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever)
Abstract
Background: Typhoid and paratyphoid are febrile illnesses, due to a bacterial infection, which remain common in many low- and middle-income countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) currently recommends the fluoroquinolone antibiotics in areas with known resistance to the older first-line antibiotics.
Objectives: To evaluate fluoroquinolone antibiotics for treating children and adults with enteric fever.
Search strategy: We searched The Cochrane Infectious Disease Group Specialized Register (February 2011); Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), published in The Cochrane Library (2011, Issue 2); MEDLINE (1966 to February 2011); EMBASE (1974 to February 2011); and LILACS (1982 to February 2011). We also searched the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) in February 2011.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials examining fluoroquinolone antibiotics, in people with blood, stool or bone marrow culture-confirmed enteric fever.
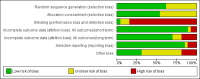
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed the trial's methodological quality and extracted data. We calculated risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous data and mean difference for continuous data with 95% confidence intervals (CI).Comparative effectiveness has been interpreted in the context of; length of treatment, dose, year of study, known levels of antibiotic resistance, or proxy measures of resistance such as the failure rate in the comparator arm.
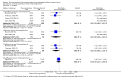
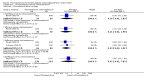
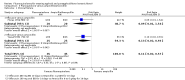
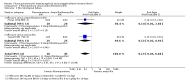
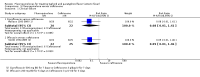
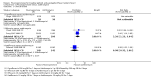
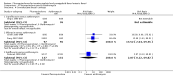
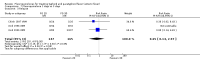
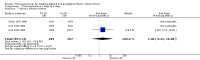
Main results: Twenty-six studies, involving 3033 patients, are included in this review.Fluoroquinolones versus older antibiotics (chloramphenicol, co-trimoxazole, amoxicillin and ampicillin)In one study from Pakistan in 2003-04, high clinical failure rates were seen with both chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole, although resistance was not confirmed microbiologically. A seven-day course of either ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin were found to be superior. Older studies of these comparisons failed to show a difference (six trials, 361 participants).In small studies conducted almost two decades ago, the fluoroquinolones were demonstrated to have fewer clinical failures than ampicillin and amoxicillin (two trials, 90 participants, RR 0.11, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.57).Fluoroquinolones versus current second-line options (ceftriaxone, cefalexin, and azithromycin)The two studies comparing a seven day course of oral fluoroquinolones with three days of intravenous ceftriaxone were too small to detect important differences between antibiotics should they exist (two trials, 89 participants).In Pakistan in 2003-04, no clinical or microbiological failures were seen with seven days of either ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin or cefixime (one trial, 139 participants). In Nepal in 2005, gatifloxacin reduced clinical failure and relapse compared to cefixime, despite a high prevalence of NaR in the study population (one trial, 158 participants, RR 0.04, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.31).Compared to a seven day course of azithromycin, a seven day course of ofloxacin had a higher rate of clinical failures in populations with both multi-drug resistance (MDR) and nalidixic acid resistance (NaR) enteric fever in Vietnam in 1998-2002 (two trials, 213 participants, RR 2.20, 95% CI 1.23 to 3.94). However, a more recent study from Vietnam in 2004-05, detected no difference between gatifloxacin and azithromycin with both drugs performing well (one trial, 287 participants).
Authors' conclusions: Generally, fluoroquinolones performed well in treating typhoid, and maybe superior to alternatives in some settings. However, we were unable to draw firm general conclusions on comparative contemporary effectiveness given that resistance changes over time, and many studies were small. Policy makers and clinicians need to consider local resistance patterns in choosing a fluoroquinolone or alternative.There is some evidence that the newest fluoroquinolone, gatifloxacin, remains effective in some regions where resistance to older fluoroquinolones has developed. However, the different fluoroquinolones have not been compared directly in trials in these settings.
Conflict of interest statement
None known. Professor ZA Bhutta has been part of trials of treatment for typhoid therapy in children, none of which involved fluoroquinolones.
Figures





















































Update of
-
Fluoroquinolones for treating typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):CD004530. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004530.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 05;(10):CD004530. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004530.pub4. PMID: 18843659 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Alam 1995 BGD {published data only}
-
- Alam MN, Haq SA, Das KK, Baral PK, Mazid MN, Siddique RU, et al. Efficacy of ciprofloxacin in enteric fever: comparison of treatment duration in sensitive and multidrug resistant salmonella. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1995;53(3):306‐11. - PubMed
Arjyal 2011 {published data only}
-
- Arjyal A, Basnyat B, Koirala S, Karkey A, Dongol S, Agrawaal KK, Shakya N, Shrestha K, Sharma M, Lama S, Shrestha K, Khatri NS, Shrestha U, Campbell JI, Baker S, Farrar J, Wolbers M, Dolecek C. Gatifloxacin versus choramphenicol: An open, randomized controlled trial in the treatment of uncomplicated enteric fever. Lancet Infect Dis 2011;11(6):445‐454. - PMC - PubMed
Chinh 1997 VNM {published data only}
-
- Chinh NT, Solomon T, Mai XT, Nguyen TL, Nguyen TT, Wain J, et al. Short courses of ofloxacin for the treatment of enteric fever. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1997;91(3):347‐9. - PubMed
Chinh 2000 VNM {published data only}
Cristiano 1995 ITA {published data only}
-
- Cirstiano P, Imparato L, Carpinelli C, Lauria F, Iovene MR, Corrado MF, et al. Pefloxacin versus chloramphenicol in the therapy of typhoid fever. Infection 1995;23(2):103‐6. - PubMed
Dolecek 2008 VNM {published data only}
Flores 1994 MEX {published data only}
-
- Flores GR, Dorantes F, Aviles J. Safety and efficacy of oral ofloxacin vs oral ampicillin in the management of typhoid. Investigacion Medica Internacional 1994;21(2):88‐92.
Gasem 2003 IDN {published data only}
-
- Gasem MH, Keuter M, Dolmans WM, Ven‐Jongekrijg J, Djokomoeljanto R, Meer JW. Persistence of Salmonellae in blood and bone marrow: randomized controlled trial comparing ciprofloxacin and chloramphenicol treatments against enteric fever. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2003;47(5):1727‐31. - PMC - PubMed
Girgis 1999 EGY {published data only}
-
- Girgis NI, Butler T, Frenck RW, Sultan Y, Brown FM, Tribble D, et al. Azithromycin versus ciprofloxacin for treatment of uncomplicated typhoid fever in a randomized trial in Egypt that included patients with multidrug resistance. Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy 1999;43(6):1441‐4. - PMC - PubMed
Gottuzzo 1992 N/A {published data only}
-
- Gottuzzo E, Carillo C. Typhoid fever. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin in comparison with chloramphenicol. In: HL Dupont editor(s). Use of quinolones in travel medicine. Second Conference on International Travel Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 1991. Berlin, Germany: Springer‐Verlag, 1992:16‐22.
Hajji 1988 MAR {published data only}
-
- Hajji M, Mdaghri N, Benbachir M, Filali KM, Himmich H. Prospective randomized comparative trial of pefloxacin versus cotrimoxazole in the treatment of typhoid fever in adults. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1988;7(3):361‐3. - PubMed
Kalo 1997 ALB {published data only}
-
- Kalo T, Davachi F, Nushi A, Dedja S, Karapici L, Como N, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of perfloxacin in treatment of ampicillin‐resistant typhoid fever in 7 days versus 10 days. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 1997;2(1):12‐4.
Limson 1989 PHL {published data only}
-
- Limson BM, Littaua RT. Comparative study of ciprofloxacin versus co‐trimoxazole in the treatment of Salmonella enteric fever. Infection 1989;17(2):105‐6. - PubMed
Morelli 1992 ITA {published data only}
-
- Morelli G, Mazzoli S, Tortoli E, Simonetti MT, Perruna F, Postiglione A. Fluoroquinolones versus chloramphenicol in the therapy of typhoid fever: a clinical and microbiological study. Current Therapeutic Research 1992;52(4):532‐42.
Pandit 2007 NPL {published data only}
Parry 2007 VNM {published data only}
-
- Parry CM, Ho VA, Phuong le T, Bay PV, Lanh MN, Tung le T, et al. Randomized controlled comparison of ofloxacin, azithromycin, and an ofloxacin‐azithromycin combination for treatment of multidrug‐resistant and nalidixic acid‐resistant typhoid fever. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 2007;51(3):819‐25. - PMC - PubMed
Phongmany 2005 LAO {published data only}
-
- Phongmany S, Phetsouvanh R, Sisouphone S, Darasavath C, Vongphachane P, Rattanavong O, et al. A randomized comparison of oral chloramphenicol versus ofloxacin in the treatment of uncomplicated typhoid fever in Laos. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2005;99(6):451‐8. - PubMed
Phuong 1999 VNM {published data only}
-
- Phuong CXT, Kneen R, Nguyen TA, Truong DL, White NJ, Parry CM. A comparative study of ofloxacin and cefixime for treatment of typhoid fever in children. The Dong Nai Pediatric Center Typhoid Study Group. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1999;18(3):245‐8. - PubMed
Rizvi 2007 PAK {published data only}
-
- Rizvi Q. Effeciveness of anti‐typhoid drugs currently used in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Surgery 2007;23(1):57‐64.
Smith 1994 VNM {published data only}
Tran 1995 VNM {published data only}
-
- Tran TH, Bethell DB, Nguyen TT, Wain J, To SD, Le TP, et al. Short course of ofloxacin for treatment of multidrug‐resistant typhoid. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1995;20(4):917‐23. - PubMed
Unal 1996 TUR {published data only}
Vinh 1996 VNM {published data only}
Vinh 2005 VNM {published data only}
-
- Vinh H, Duong NM, Phuong lT, Truong NT, Bay PV, Wain J, et al. Comparative trial of short‐course ofloxacin for uncomplicated typhoid fever in Vietnamese children. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2005;25(1):17‐22. - PubMed
Wallace 1993 BHR {published data only}
-
- Wallace MR, Yousif AA, Mahroos GA, Mapes T, Threlfall EJ, Rowe B, et al. Ciprofloxacin versus ceftriaxone in the treatment of multiresistant typhoid fever. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1993;12(12):907‐10. - PubMed
Yousaf 1992 PAK {published data only}
-
- Yousaf MH, Hasnain SS, Mohsin A, Ara N. A comparative study of efficacy and safety of three antimicrobials in the treatment of enteric fever. Pakistan Journal of Gastroenterology 1992;6(2):46‐8.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abejar 1993 {published data only}
-
- Abejar NH, Dimaano EM, Cabanban AB. Fleroxacin versus chloramphenicol in enteric fever. An open, randomized, parallel study. Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine 1993;31(6):327‐30.
Agalar 1997 {published data only}
-
- Agalar C, Usubutun S, Tutuncu E, Turkyilmaz R. Comparison of two regimens for ciprofloxacin treatment of enteric infections. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1997;16(11):803‐6. - PubMed
Akhtar 1989 {published data only}
-
- Akhtar MA, Karamat KA, Malik AZ, Hashmi A, Khan QM, Rasheed P. Efficacy of ofloxacin in typhoid fever, particularly in drug resistant cases. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1989;2 Suppl 5:1193.
Akhtar 1992 {published data only}
-
- Akhtar MA, Hussain A, Karamat KA, Naqi N, Zubdi N. Role of ciprofloxacin in typhoid fever. Journal of Pakistan Medical Association 1992;42(1):9‐10. - PubMed
Arnold 1993 {published data only}
-
- Arnold K, Hong C, Nelwan R, Trujillo Z, Kadio A, Barros M, et al. Randomized comparative study of fleroxacin and chloramphenicol in typhoid fever. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(3A):195S‐200S. - PubMed
Bai 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bai YM, Lin JB, Duan MT, Zhang Y, Liang B. Comparison of therapeutic effect of enoxacin and norfloxacin in the treatment of typhoid fever. Zhonghua Chuan Ran Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases] 1995;13(2):117‐8.
Bavdekar 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bavdekar A, Chaudhari M, Bhave S, Pandit A. Ciprofloxacin in typhoid fever. Indian Journal Pediatrics 1991;58(3):335‐9. - PubMed
Bethell 1996 {published data only}
Chakravorty 1991 {published data only}
-
- Chakravorty B, Jain N, Gupta B, Rajvanshi P, Sen MK, Krishna A. Chloramphenicol resistant enteric fever. Journal of Indian Medical Association 1993;91(1):10‐13. - PubMed
Chukwani 1998 {published data only}
-
- Chukwani CM, Onyemelukwe GC, Okonkwo PO, Coker HAB, Ifudu ND. Fleroxacin vs ciprofloxacin in the management of typhoid fever. Clinical Drugs Investigation 1998;16(4):279‐88. - PubMed
Daga 1994 {published data only}
-
- Daga MK, Sarin K, Sarkar R. A study of culture positive multidrug resistant enteric fever ‐ changing pattern and emerging resistance to ciprofloxacin. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1994;42(8):599‐600. - PubMed
Duong 1995 {published data only}
-
- Duong NM, Chau NVV, Anh DCV, Hoa NTT, Tam DTH, Hai DT, et al. Short course fleroxacin in the treatment of typhoid fever. JAMA Southeast Asia 1995;11 Suppl:21‐5.
Hou 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hou SR. Clinical study of Chinese ofloxacin. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1993;73(4):255‐6. - PubMed
Huai 2000 {published data only}
-
- Huai Y, Zhu Q, Wang X. Ceftriaxone vs. norfloxacin in the treatment of resistant typhoid fever in 60 children. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Pediatrics] 2000;38(6):386‐8.
Jia 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jia FZ, Zhu JQ, Huang SY, Chen HK, Bai JY, Li ZC, et al. Clinical study on therapy of typhoid fever with pefloxacin. Zhonghua Chuan Ran Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases] 1994;12 Suppl 3:134‐6.
Jinlong 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jinlong Z, Wennan H, Guosheng M, Zhigang H, Jianping Z. Evaluation of effectiveness of ofloxacin and S‐(‐) ofloxacin in treating typhoid fever. Zhonghua Chuan Ran Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases] 1998;16(4):237.
Kumar 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kumar R, Gupta N. Multidrug‐resistant typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2007;74(1):39‐42. - PubMed
Liberti 2000 {published data only}
-
- Liberti A, Loiacono L. Ciprofloxacin versus chloramphenicol in the treatment of salmonella infection. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2000;16(3):347‐8. - PubMed
Lu 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lu Y, Zhang H, Mu G, Qiu D, Hu P. Clinical study of intravenous enoxacin versus cefotaxime in aute [sic] infectious diseases. Zhongguo Kang Sheng Su Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Antibiotics] 1995;20(2):123‐8.
Nalin 1987 {published data only}
-
- Nalin DR, Hoagland VL, Acuna G, Bran JL, Carrilo C, Gotuzzo E, et al. Clinical trial of norfloxacin versus chloramphenicol therapy for acute typhoid fever. Progress in antimicrobial and anti‐cancer chemotherapy. Proceedings of the 15th International Congress of Chemotherapy; 1987 July 19‐24; Istanbul. Copenhagen, Munksgaard, 1987:1174‐5.
Nelwan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nelwan RH, Hendarwanto, Zulkarnain I, Gunawan J, Supandiman I, Yusuf H, et al. A comparative study of short course ciprofloxacin treatment in typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Drugs 1995;49 Suppl 2:463‐5. - PubMed
Peyramond 1986 {published data only}
-
- Peyramond D, Tiguad S, Lucht F, Vedrinne JM, Salord F, Bertrand JL. Clinical evaluation of ofloxacin in the treatment of various infections [Bilan d'utilisation de l'ofloxacine dans le traitement d'infections variées]. Pathologie‐Biologie 1986;34(5):471‐5. - PubMed
Sarma 1991 {published data only}
-
- Sarma PS, Durairaj P. Randomized treatment of patients with typhoid and paratyphoid fevers using norfloxacin or chloramphenicol. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;85(5):670‐1. - PubMed
Secmeer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Secmeer G, Kanra G, Figen G, Akan O, Ceyhan M, Ecevit Z. Ofloxacin versus co‐trimoxazole in the treatment of typhoid fever in children. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1997;39(2):218‐21. - PubMed
Singh 1993 {published data only}
-
- Singh CP, Singh N, Brar GK, Lal G, Kumar H. Efficacy of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin in multidrug resistant enteric fever in adults. Journal of the Indian Medical Association 1993;91(6):156‐7. - PubMed
Suhendro 2007 {published data only}
-
- Suhendro, Chen K, Pohan HT. Open study on efficacy and tolerability of ciprofloxacin XR compared with ciprofloxacin BID in the treatment of typhoid fever. Acta Medica Indonesiana 2007;39(1):22‐6. - PubMed
Takkar 1994 {published data only}
-
- Takkar VP, Kumar R, Khurana S, Takkar R. Comparison of ciprofloxacin versus cephelexin and gentamicin in the treatment of multi‐drug resistant typhoid fever. Indian Pediatrics 1994;31(2):200‐1. - PubMed
Tanphaichitra 1986 {published data only}
-
- Tanphaichitra D, Sahaphong S, Srimuang S. Ofloxacin, a new quinolone in the treatment of genitourinary and enteric infections. Infection 1986;14 Suppl 4:321‐3. - PubMed
Tran 1994 {published data only}
-
- Tran TH, Nguyen MD, Huynh DH, Nguyen TT, To SD, Le TP, et al. A randomized comparative study of fleroxacin and ceftriaxone in enteric fever. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1994;88(4):464‐5. - PubMed
Uwaydah 1992 {published data only}
-
- Uwaydah AK, al Soub H, Matar I. Randomized prospective study comparing two dosage regimens of ciprofloxacin for the treatment of typhoid fever. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1992;30(5):707‐11. - PubMed
Wain 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wain J, Hoa NTT, Chinh NT, Vinh H, Everett J, Diep TS, et al. Quinolone‐resistant Salmonella typhi in Viet Nam: molecular basis of resistance and clinical response to treatment. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1997;25(6):1404‐10. - PubMed
Weng 1996a {published data only}
-
- Weng YL, Jia FZ. Clinical efficacy evaluation of fluoroquinolones in typhoid fever (clinical analysis of 391 cases). Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1996;12(3):142‐7.
Yang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Yang JG, Wa XL, Shen XJ, Wang KL, Zhu XB, Chen ZY. Short course of ofloxacin in the treatment of 28 patients of typhoid fever. Xin Yao Yu Lin Chuang [New Drugs and Clinical Remedies] 1991;11(2):79‐80.
Zavala 1989 {published data only}
-
- Zavala‐Trujillo I, Nava‐Zavala A, Marcano MG, Renteria M. Fleroxacin in the treatment of enteric fever and salmonellosis in adults. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1989;2 Suppl 5:1188‐9.
Zhang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Zhang YY, Zhun BY, Jiang SC. Clinical evaluation of enoxacin. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine] 1991;30(8):480‐3, 521. - PubMed
ZhongYang 1997 {published data only}
-
- ZhongYang H, Zheng L, Xinchung L, Hanjun H, Yi L X. Compared observation on therapeutic effect of ofloxacin and norfloxacin in treatment of typhoid fever. Zhonghua Chuan Ran Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases] 1997;15(4):229‐30.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bran 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bran JL, Garcia JF, Mendez O. Comparative, double blind study of chloramphenicol and ciprofloxacin in the treatment of typhoid fever (abstract 751). Proceedings of the 31st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 1991 Sept 29‐Oct 2; Chicago, Illinois. Washington, DC: American Society of Microbiology, 1991:224.
Flores 1991 {published data only}
-
- Flores GR. Pharmacological treatment of typhoid fever: A comparative study of ciprofloxacin versus trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole [Tratamiento farmacológico del paciente con fiebre tifoidea: estudio comparativo entre ciprofloxacina y trimetoprim‐sulfametoxazol]. Investigacion Medica International 1991;17(4):185‐8.
Quintero 1988 {published data only}
-
- Quintero‐Perez NP, Andrea‐Villanueva J, Leon‐Garnica M, Bertin‐Montano M, Chagollan‐Rodriguez E, Rodiguez‐Noriega E. Comparative double blind efficacy and safety study of ciprofloxacin with chloramphenicol in the treatment of typhoid fever. Abstract number 385. Programs and abstracts of the 28th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 1988 Oct 23‐26; Los Angeles, California. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, 1988:177.
Soewandojo 1992 {published data only}
-
- Soewandojo E, Suharto JR. Comparative study of ciprofloxacin vs chloramphenicol in patients with typhoid fever. Typhoid fever, profile, diagnosis and treatment in 1990. Proceedings of the 1st ISAC International Symposium. Jakarta: Acta Medica Indonesia, 1992:119‐25.
Weng 1996 {published data only}
-
- Weng Y‐L, Jia F‐Z. Clinical efficacy evaluation of fluoroquinolones in typhoid fever (clinical analysis of 391 cases). Zhongguo Lin Chuang Yao Li Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology] 1996;12(3):142‐7.
Xiao 1991 {published data only}
-
- Xiao YH, Wang QN, Du JZ, Zheng XP, Li ZZ, Qui J, et al. Clinical and laboratory study of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics in the treatment of multiresistant typhoid fever. Sichuan I Hseuh 1991;12(4):196‐8.
Yu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Yu Y‐S, Zheng J‐C, Gan M‐J, Ma Y‐L. Clinical study on the efficacy and safety of the levofloxacin used to treat the patients with typhoid fever or paratyphoid fever. Zhongguo Lin Chuang Yao Li Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology] 1998;14(2):70‐4.
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN66534807 {unpublished data only}
-
- ISRCTN66534807. A randomised clinical trial of Azithromycin versus Ofloxacin in the treatment of adults with uncomplicated typhoid fever at Mahosot Hospital, Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic (PDR). www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN66534807.
Additional references
Ackers 2000
-
- Ackers ML, Puhr ND, Tauxe RV, Mintz ED. Laboratory‐based surveillance of Salmonella serotype Typhi infections in the United States: antimicrobial resistance on the rise. JAMA 2000;283(20):2668‐73. - PubMed
Adachi 2005
Ahmad 2002
-
- Ahmad K. Experts call for surveillance of drug‐resistant typhoid at a global level. Lancet 2002;359(9306):592. - PubMed
Ahmed 2006
Akinyemi 2005
-
- Akinyemi KO, Smith SI, Oyefolu AOB, Coker AO. Multidrug resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhi isolated from patients with typhoid fever complications in Lagos, Nigeria. Public Health 2005;119(4):321‐7. - PubMed
Ambrose 2003
-
- Ambrose PG, Bhavnani SM, Cirincione BB, Piedmonte M, Grasela TH. Gatifloxacin and the elderly: pharmacokinetic‐pharmacodynamic rationale for a potential age‐related dose reduction. Journal of Antimicrobial and Chemotherapy 2003;52:435‐40. - PubMed
Bertino 2000
-
- Bertino J, Fish D. The Safety Profile of the Fluoroquinolones. Clinical Therapeutics 2000;22(7):798‐817. - PubMed
Bhan 2005
-
- Bhan MK, Bahl R, Bhatnagar S. Typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Lancet 2005;366(9487):749‐62. - PubMed
Bhutta 1996
Brooks 2005
BSAC 2011
-
- British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. BASC methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, version 10, January 2011. Bristish Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, Birmingham, United Kingdom. http://www.bsac.org.uk/Resources/BSAC/Version%20%2010%202011%20final.pdf.
Butt 2005
-
- Butt T, Ahmad RN, Salman M, Kazmi SY. Changing trends in drug resistance among typhoid salmonellae in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal 2005;11(5‐6):1038‐44. - PubMed
Chandel 2000
Chuang 2009
-
- Chuang CH, Su LH, Perera J, Carlos C, Tan BH, Kumarasinghe G, et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi in seven Asian countries. Epidemiology and Infection 2009;137(2):266‐9. - PubMed
CLSI 2007
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Seventeenth Informational Supplement 2007;27:MS100‐S17.
Committee 2006
-
- Committee on Infectious Diseases. The use of systemic fluoroquinolones. Pediatrics 2006;118(3):1287‐92. - PubMed
Congeni 2002
-
- Congeni BL, Thomson RB Jr. Fluoroqinolones: consideration for future use. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 2002;21(4):345‐6. - PubMed
Cooke 2006
Cooke 2007
-
- Cooke FJ, Day M, Wain J, Ward LR, Threlfall EJ. Cases of typhoid fever imported into England, Scotland and Wales (2000–2003). Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;101(4):398‐404. - PubMed
Coovadia 1992
-
- Coovadia YM, Gathiram V, Bhamjee A, Garratt RM, Mlisana K, Pillay N, et al. An outbreak of multiresistant Salmonella typhi in South Africa. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1992;82(298):91‐100. - PubMed
Crump 2003
-
- Crump JA, Barrett TJ, Nelson JT, Angulo FJ. Reevaluating fluoroquinolone breakpoints for salmonella enterica typhi and for non‐Typhi salmonellae. Clinical Infectious Disease 2003;37:75‐81. - PubMed
Crump 2004
Crump 2008
-
- Crump JA, Kretsinger K, Gay K, Hoekstra RM, Vugia DJ, Hurd S. Clinical response and outcome of infection with Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi with decreased susceptibility to fluoroquinolones: a United States foodnet multicenter retrospective cohort study. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2008;52:1278‐84. - PMC - PubMed
Dimitrov 2009
Fish 2001
-
- Fish DN. Fluoroquinolone adverse effects and drug interactions. Pharmacotherapy 2001;21(10 Part 2):253‐72. - PubMed
Frothingham 2005
-
- Frothingham R. Glucose homeostasis abnormalities associated with use of gatifloxacin. Clinical Infectious Disease 2005;41:1269‐76. - PubMed
Fukuda 2001
Gaind 2006
-
- Gaind R, Paglietti B, Murgia M, Dawar R, Uzzau S, Cappuccinelli P, et al. Molecular characterization of ciprofloxacin‐resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and Paratyphi A causing enteric fever in India. Journal of Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy 2006;58(6):1139‐44. - PubMed
Gupta 2009
-
- Gupta V, Kaur J, Kaistha N. Re‐emerging chloramphenicol sensitivity and emerging low level ciprofloxacin resistance among Salmonella enterica serotype typhi isolates in North India. Tropical Doctor 2009;39(1):28‐30. - PubMed
Harish 2004
-
- Harish BN, Madhulika U, Parija SC. Isolated high‐level ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serotype Paratyphi A. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2004;53(Pt 8):819. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration. www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm 2011.
Hooper 2000
-
- Hooper DC. Quinolones. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R editor(s). Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 5th Edition. Philadelphia. London: Churchill Livingstone, 2000:405‐20.
Ivanoff 1995
-
- Ivanoff B. Typhoid fever: global situation and WHO recommendations. Southeast Asian Journal of Topical Medicine and Public Health 1995;26 Suppl 2:1‐6.
Jesudason 2005
-
- Jesudason MV. Paratyphoid fever in Vellore, South India. Tropical Doctor 2005;35(3):191. - PubMed
Joshi 2007
-
- Joshi S, Amarnath SK. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella typhi and S. paratyphi A in Bangalore, India. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;101(3):308‐10. - PubMed
Kariuki 2004
Keddy 2010
Kownhar 2007
-
- Kownhar H, Shankar EM, Rajan R, Rao UA. Emergence of nalidixic acid‐resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi resistant to ciprofloxacin in India. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2007;56(1):136‐7. - PubMed
Lakshmi 2006
-
- Lakshmi V, Ashok R, Susmita J, Shailaja VV. Changing trends in the antibiograms of Salmonella isolates at a tertiary care hospital in Hyderabad. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology 2006;24(1):45‐8. - PubMed
Lee 2000
-
- Lee TP, Hoffman SL. Typhoid fever. In: Strickland GT editor(s). Hunter's Tropical medicine and emerging infectious diseases. 8th Edition. Philadelphia. London: Saunders, 2000:471‐83.
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies.. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Lesser 2001
-
- Lesser CF, Miller SI. Salmonellosis. In: Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL editor(s). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 15th Edition. Vol. 1, New York: McGraw‐Hill, 2001:971‐3.
Lin 2000
-
- Lin FY, Vo AH, Phan VB, Nguyen TT, Bryla D, Tran CT, et al. The epidemiology of typhoid fever in the Dong Thap Province, Mekong Delta region of Vietnam. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2000;62(5):644‐8. - PubMed
Maskey 2008
-
- Maskey AP, Basnyat B, Thwaites GE, Campbell JI, Farrar JJ, Zimmerman MD. Emerging trends in enteric fever in Nepal: 9124 cases confirmed by blood culture 1993‐2003. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2008;102:91‐5. - PubMed
McNabb 2008
-
- McNabb SJ, Jajosky RA, Hall‐Baker PA, Adams DA, Sharp P, Worshams C, et al. Centersfor Disease Control and Prevention. Summary of notifiable diseases ‐ United States, 2006. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Reports 2008;55(53):1‐92. - PubMed
Medalla 2011
Mermin 1999
-
- Mermin JH, Villar R, Carpenter J, Roberts L, Samaridden A, Gasanova L, et al. A massive epidemic of multidrug‐resistant typhoid fever in Tajikistan associated with consumption of municipal water. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1999;179(6):1416‐22. - PubMed
Miller 2000
-
- Miller SI, Pegues DA. Salmonella species, including Salmonella typhi. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R editor(s). Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 5th Edition. Philadelphia. London: Churchill Livingstone, 2000:2344‐56.
Mohanty 2006
Ochiai 2005
Ochiai 2008
Oliphant 2002
-
- Oliphant CM, Green GM. Quinolones; A Comprehensive Review. American Family Physician 2002;65(3):455‐64. - PubMed
Park‐Wyllie 2006
-
- Park‐Wyllie LY, Juurlink DN, Kopp A, Shah BR, Stukel TA, Stumpo C, et al. Outpatient gatifloxacin therapy and dysglycemia in older adults. NEJM 2006;354:1352‐61. - PubMed
Parry 2002
-
- Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, Whilte NJ, Farrar JJ. Typhoid fever. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(22):1770‐82. - PubMed
Parry 2006
Parry 2010
Renuka 2005
-
- Renuka K, Sood S, Das BK, Kapil A. High‐level ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi in India. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2005;54(Pt 10):999‐1000. - PubMed
Review Manager 5.1 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager. Version 5.1 for Windows. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Richens 2000
-
- Richens J. Typhoid fever. In: Armstrong D, Cohen J editor(s). Infectious diseases. 1st Edition. London: Mosby, 2000:6‐24.1‐4.
Rodrigues 2003
-
- Rodrigues C, Shenai S, Mehta A. Enteric fever in Mumbai, India: the good news and the bad news. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2003;36(4):535. - PubMed
Rupali 2004
-
- Rupali P, Abraham OC, Jesudason MV, John TJ, Zachariah A, Sivaram S, et al. Treatment failure in typhoid fever with ciprofloxacin susceptible Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2004;49(1):1‐3. - PubMed
Saha 2001
-
- Saha SK, Baqui AH, Hanif M, Darmstadt GL, Ruhulamin M, Nagatake T, et al. Typhoid fever in Bangladesh: implications for vaccination policy. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 2001;20(5):521‐4. - PubMed
Saha 2003
-
- Saha MR, Dutta P, Palit A, Dutta D, Bhattacharya MK, Mitra U, et al. A note on incidence of typhoid fever in diverse age groups in Kolkata, India. Japan Journal of Infectious Diseases 2003;56(3):121‐2. - PubMed
Siddiqui 2006
-
- Siddiqui FJ, Rabbani F, Hasan R, Nizami SQ, Bhutta ZA. Typhoid fever in children: some epidemiological considerations from Karachi, Pakistan. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2006;10(3):215‐22. - PubMed
Sinha 1999
-
- Sinha A, Sazawal S, Kumar R, Sood S, Reddaiah VP, Singh B, et al. Typhoid fever in children aged less than 5 years. Lancet 1999;354(9180):734‐7. - PubMed
Smith 2010
-
- Smith AM, Govender N, Keddy KH. Quinolone resistant Salmonella Typhi in South Africa, 2003‐2007. Epiemiology and Infection 2010;138:86‐90. - PubMed
Sood 1999
-
- Sood S, Kapil A, Das B, Jain Y, Kabra SK. Re‐emergence of chloramphenicol‐sensitive Salmonella typhi. Lancet 1999;353(9160):1241‐2. - PubMed
Sur 2006
-
- Sur D, von SL, Manna B, Dutta S, Deb AK, Sarkar BL, et al. The malaria and typhoid fever burden in the slums of Kolkata, India: data from a prospective community‐based study. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;100(8):725‐33. - PubMed
Takkar 1995
-
- Takkar VP, Kumar R, Takkar R, Khurana S. Resurgence of chloramphenicol sensitive Salmonella typhi. Indian Pediatrics 1995;32(5):586‐7. - PubMed
Threlfall 1999
-
- Threlfall EJ, Ward LR, Skinner JA, Smith HR, Lacey S. Ciprofloxacin‐resistant Salmonella typhi and treatment failure. Lancet 1999;353(9164):1590‐1. - PubMed
Threlfall 2003
-
- Threlfall EJ, Fisher IS, Berghold C, Gerner‐Smidt P, Tschape H, Cormican M, et al. Trends in antimicrobial drug resistance in Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhi and Paratyphi A isolated in Europe, 1999‐2001. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2003;22(5):487‐91. - PubMed
Walia 2005
-
- Walia M, Gaind R, Mehta R, Paul P, Aggarwal P, Kalaivani M. Current perspectives of enteric fever: a hospital‐based study from India. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2005;25(3):161‐74. - PubMed
Walia 2006
-
- Walia M, Gaind R, Paul P, Mehta R, Aggarwal P, Kalaivani M. Age‐related clinical and microbiological characteristics of enteric fever in India. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;100(10):942‐8. - PubMed
Wasfy 2002
-
- Wasfy MO, Frenck R, Ismail TF, Masour H, Malone JL, Mahoney FJ. Trends of multiple‐drug resistance among Salmonella serotype Typhi isolates during a 14‐year period in Egypt. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2002;35(10):1265‐8. - PubMed
Woods 2006
-
- Woods CW, Murdoch DR, Zimmerman MD, Glover WA, Basnyat B, Wolf L, et al. Emergence of Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi A as a major cause of enteric fever in Kathmandu, Nepal. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;100(11):1063‐7. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Thaver 2008
-
- Thaver DA, Zaidi AK, Critchley JA, Azmatullah A, Madni SA, Bhutta ZA. Fluoroquinolones for treating typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008;4:CD004530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

