Combination therapy for pain management in inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, other spondyloarthritis)
- PMID: 21975788
- PMCID: PMC12416524
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008886.pub2
Combination therapy for pain management in inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, other spondyloarthritis)
Abstract
Background: Despite optimal therapy with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, many people with inflammatory arthritis (IA) continue to have persistent pain that may require additional therapy.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and safety of combination pain therapy for people with IA (rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and other spondyloarthritis (SpA)). We planned to assess differences in effects between patients on background disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy and patients on no background therapy in subgroup analyses.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library); MEDLINE; and EMBASE. We did not impose any date or language restrictions in the search. We also handsearched conference proceedings of the American College of Rheumatology and the European League against Rheumatism (2008-10).
Selection criteria: Randomised and controlled clinical trials (RCTs and CCTs) assessing combination therapy (at least two drugs from the following classes: analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, opioid-like drugs and neuromodulators (antidepressants, anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants)) compared with monotherapy, for adults with IA (RA, AS, PsA and other SpA). We speficically excluded studies that did not report pain or studies without a standardised pain scale as an outcome measure.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected trials for inclusion, assessed risk of bias and extracted data.
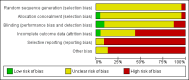
Main results: Twenty-three trials (total of 912 patients) met the inclusion criteria (22 in RA; one in a mixed population of RA and osteoarthritis); all except one were published before 1990. Most study populations were not taking DMARDs (e.g. methotrexate, sulphasalazine, hydroxychloroquine and leflunomide) and all studies were performed prior to the introduction of biologic therapies (e.g. etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab). All trials were at high risk of bias, heterogeneity precluded meta-analysis, and we were only able to report a general description of results.The majority (18 studies, 78%) found no differences between the combination and monotherapy treatments they studied, while five (22%) reported conflicting results, favouring either the combination or monotherapy arms.From the 12 trials on NSAID + analgesic vs NSAID, nine reported no significant difference between the interventions, while three did: in two, the combination therapy achieved better pain control; and the third trial compared combination therapy with two different dosages of monotherapy (NSAID alone) and reported that a high dose phenylbutazone was superior to combination therapy (paracetamol + aspirin), which was superior to low dose phenylbutazone.From the five studies on the combination of two NSAIDS vs one NSAID, four reported no significant differences between interventions, and one reported significantly better pain control with combination therapy.The single trial comparing a combination of opioid + neuromodulator vs opioid reported better pain control with monotherapy.The remaining trials (NSAID + neuromodulator vs NSAID (3 trials); opioid + NSAID vs NSAID (1 trial); and opioid + analgesic vs analgesic (1 trial)) found no significant difference between combination therapy and monotherapy.Information regarding withdrawals due to inadequate analgesia and safety was incompletely reported, but in general there were no differences between combination therapy and monotherapy.No data were available that addressed the value of combination pain therapy or monotherapy for people with IA who have optimal disease suppression. There were no studies that included patients with AS, PsA or SpA.
Authors' conclusions: Based on 23 trials, all at high risk of bias, there is insufficient evidence to establish the value of combination therapy over monotherapy for people with IA. Importantly, there are no studies addressing the value of combination therapy for patients with IA who have persistent pain despite optimal disease suppression. Well designed trials are needed to address this question.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Beales 1972 {published data only}
Bedi 1969 {published data only}
-
- Bedi SS. Comparison of aspirin and dextropropoxyphene‐with‐aspirin as analgesics in rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1969;23(10):413‐7. - PubMed
Brooks 1975 {published data only}
-
- Brooks PM, Walker JJ, Lee P, Bell AM, Buchanan WW, Fowler PD, et al. Clinical study on a new acetylsalicylic acid/paracetamol preparation with gastric acid resistant coating (Safapryn), and on two various phenylbutazone dosages in patients with primary chronic polyarthritis as based on a new evaluation method [Erprobung eines neuen acetylsalicylsäure/paracetamol‐präparates mit magensaftresistentem Überzug (Safapryn) und zwei verschiedenen Dosierungen von Phenylbutazon bei Patienten mit primär chronischer Polyarthritis anhand eines neuen Bewertungsverfahrens]. Zeitschrift fur Rheumatologie 1975;34(9‐10):350‐65. - PubMed
Coigley 1975 {published data only}
-
- Coigley MH. Comparison of benorylate and indomethacin in the symptomatic control of arthritic disorders. Practitioner 1975;215(1287):348‐52. - PubMed
Ekstrand 1981 {published data only}
-
- Ekstrand R, Alvan G, Magnusson A, Oliw E, Palmer L, Rane A. Additive clinical effect of indomethacin suppositories during salicylate therapy in rheumatoid patients. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1981;10(2):69‐75. - PubMed
Furst 1987 {published data only}
-
- Furst DE, Blocka K, Cassell S, Harris ER, Hirschberg JM, Josephson N, et al. A controlled study of concurrent therapy with a nonacetylated salicylate and naproxen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1987;30(2):146‐54. - PubMed
Grennan 1979 {published data only}
Haslock 1971 {published data only}
-
- Haslock DI, Nicholson PA, Wright V. A comparison of phenylbutazone and benorylate. Clinical Trials Journal 1971;8(1):43‐50.
Hingorani 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hingorani K. Double blind study of benorylate and ibuprofen in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 1973;12(suppl):39‐47.
Hobkirk 1977 {published data only}
-
- Hobkirk D, Rhodes M, Haslock I. Night medication in rheumatoid arthritis: II. Combined therapy with indomethacin and diazepam. Rheumatology & Rehabilitation 1977;16(2):125‐7. - PubMed
Huskisson 1974 {published data only}
Kean 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kean WF, Kraag GR, Rooney PJ, Capell HA. Clinical therapeutic trial of aspirin and azapropazone in rheumatoid arthritis when prescribed singly and in combination. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1981;7(3):164‐7. - PubMed
Malcolm 1974 {published data only}
-
- Malcolm A. A comparative clinical trial of benorylate and indomethacin in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis in general practice. Journal of International Medical Research 1974;2(1):66‐70.
Mavrikakis 1977a {published data only}
-
- Mavrikakis ME, McLeod M, Hernandez LA, El‐Ghobarey AF, Cappel HA. Comparison of benorylate tablets with ibuprofen in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmatherapeutica 1977;1(9):621‐4.
Mavrikakis 1977b {published data only}
-
- Mavrikakis ME, Madkour MM, Spencer DM, Balint GP. Double‐blind study comparing the therapeutic effect of a new non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drug, sulindac, with benorylate in tablet form in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmatherapeutica 1977;1(10):681‐5.
Mowat 1979 {published data only}
-
- Mowat AM, Mowat AG. A comparative trial of naproxen and benorylate suspensions in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation 1979;2(1):74‐8.
Puttini 1988 {published data only}
-
- Puttini P, Cazzola M, Boccassini L, Ciniselli G, Santandrea S, Caruso I, et al. A comparison of dothiepin versus placebo in the treatment of pain in rheumatoid arthritis and the association of pain with depression. The Jounal of International Medical Research 1988;16(5):331‐7. - PubMed
Saarialho‐Kere 1988 {published data only}
-
- Saarialho‐Kere U, Julkunen H, Mattila M, Seppälä T. Psycomotor performance of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: cross‐over comparison of dextroproproxyphene, dextropropoxyphene plus amitriptyline, indomethacin, and placebo. Pharmacology and Toxicology 1988;63(4):286‐92. - PubMed
Seideman 1988 {published data only}
-
- Seideman P, Melander A. Equianalgesic effects of paracetamol and indomethacin in rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Rheumatology 1988;27(2):117‐22. - PubMed
Seideman 1993 {published data only}
-
- Seideman P. Additive effect of combined naproxen and paracetamol in rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Rheumatology 1993;32(12):1077‐82. - PubMed
Sharma 1978 {published data only}
-
- Sharma BK, Haslock I. Night medication in rheumatoid arthritis. III. the use of sulindac. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1978;5(6):472‐5. - PubMed
Sperryn 1973 {published data only}
Staunton 1980 {published data only}
-
- Staunton Smith G, Moran CJ. Diflunisal plus indomethacin as concomitant therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation 1980;3(3):187‐93.
References to studies excluded from this review
Andrade‐Padilla 1995 {published data only}
-
- Andrade‐Padilla JM, Aguilar JA, Reynoso P, Romero Guillermo, Oritiz D. Double‐blind trial with ketoprophene + chlorzoxazone and ketoprophene in most frequent osteomuscular problems in the outpatient practice [Estudio doble ciego con ketoprofeno + clorzoxazona y ketoprofeno en problemas osteomusculares más frecuentes en la consulta externa]. Investigacion Medica Internacional 1995;22:52‐7.
Bain 1970 {published data only}
-
- Bain LJS, Burt RAP. The treatment of rheumatoid disease. A double blind trial comparing buffered aspirin with benorylate. Clinical Trials Journal 1970;7(2):307‐12.
Barnardo 1966 {published data only}
Brooks 1977 {published data only}
-
- Brooks PM, Khong TK. Flurbiprofen‐aspirin interaction: a double‐blind crossover study. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1977;5(1):53‐7. - PubMed
Cardoe 1970 {published data only}
-
- Cardoe N. The treatment of rheumatoid disease. Preliminary assessment of a new drug: benorylate. Clinical Trials Journal 1970;7:173‐8.
Chalmers 1978 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers A, Offer R, Robinson HS. A double‐blind controlled study comparing the use of ASA and tolmetin with ASA and placebo in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Current Therapeutic Research ‐ Clinical and Experimental 1978;24:517‐23.
Dalmases 1966 {published data only}
-
- Dalmases R, Heredia J, Cots R. Association of butazolidin with other non‐steroid drugs in the treatment of chronic evolutive polyarthritis [Associación de butazolidina con otros medicamentos no esteroideos en el tratamiento de la P.C.P]. Revista Espanola de Reumatismo y Enfermedades Osteo‐Articulares 1966;11(8):40‐3. - PubMed
De Mattos 1968 {published data only}
-
- Mattos H. Use of paracetamol‐phenylbutazone combination in rheumatic diseases of professional motorists [Uso da associação paracetamol‐fenilbutazona em afecções reumáticas de motoristas profissionais]. Hospital 1968;74(2):543‐8. - PubMed
Eberl 1968 {published data only}
-
- Eberl R. Additional treatment of rheumatologic diseases with Arcobutina ointment. Hippokrates 1968;39(18):710‐1. - PubMed
Famaey 1971 {published data only}
-
- Famaey JP, Colinet E. Cooperative study of the combination bufexamac‐alclofenac in rheumatic diseases [Etude clinique de l'association bufexamac ‐ alclofenac dan less affections d'origine rhumatismale]. Journal Belge de Rhumatologie et de Medecine Physique ‐ Belgisch Tijdschrift voor Reumatologie en Fysische Geneeskunde 1971;26(6):297‐311. - PubMed
Famaey 1972 {published data only}
-
- Famaey JP, Bauduin MP, Wanet G. Combined alclofenac‐bufexamac in rheumatology [L'association alclofenac‐bufexamac en rhumatologie]. Journal Belge de Rhumatologie et de Medecine Physique ‐ Belgisch Tijdschrift voor Reumatologie en Fysische Geneeskunde 1972;27(3):110‐19. - PubMed
France 1968 {published data only}
-
- France O. Combination of ketophenylbutazone (Ketason), oxyphenbutazone and proteolytic enzymes in rheumatic diseases [Associacion de Cetofenilbutazone (Ketazon) oxifenbutazona y enzimas proteoliticas en afecciones reumaticas]. Revista Medica de Chile 1968;96(8):531‐4. - PubMed
Franke 1972 {published data only}
-
- Franke M, Manz G. Benorylate and indomethacin in the treatment of rheumatoid disease: a double‐blind clinical trial. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1972;14(3):113‐22. - PubMed
Glowinski 1999 {published data only}
-
- Glowinski JBE. Placebo‐controlled study of the analgesic efficacy of a paracetamol 500 mg/Codeine 30 mg combination together with low‐dose vs high‐dose diclofenac in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Drug Investigation 1999;18(3):189‐97.
Hernandez Pena 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hernandez Pena M. Clinical experience with an indomethacin‐phenylbutazone combination in various rheumatic diseases [Experiencia clinica con la asociacion indometacina‐fenilbutazona en algunas afecciones reumaticas]. Revista Espanola de Reumatismo y Enfermedades Osteo‐Articulares 1973;16(2):111‐31. - PubMed
Hersh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hersh EV, Pinto A, Moore PA. Adverse drug interactions involving common prescription and over‐the‐counter analgesic agents. Clinical Therapeutics 2007;29(11 Suppl):2477‐97. - PubMed
Huss 1974 {published data only}
-
- Huss V. Combined drug therapy in highly acute attacks of pain in the course of rheumatic diseases [Kombinierte medikamentöse Behandlung hochakuter Schmerzschübe im Verlaufe rheumatischer Erkrankungen]. MMW ‐ Munchener Medizinische Wochenschrift 1974;116(27):1323‐4. - PubMed
Jaffé 1973 {published data only}
-
- Jaffe G. Treatment of arthritis in general practice. A comparison between benorylate and indomethacin. Journal of International Medical Research 1973;1(3):166‐71.
Jeremy 1970 {published data only}
-
- Jeremy R, Towson J. Interaction between aspirin and indomethacin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Medical Journal of Australia 1970;2(3):127‐9. - PubMed
Lewis‐Faning 1972 {published data only}
-
- Lewis Faning E, Wilkinson PM. The treatment of rheumatic and degenerative arthritis. A double blind trial of tandalgesic and aspirin. Clinical Trials Journal 1972;9(2):23‐9.
Lopez Prats 1968 {published data only}
-
- Lopez Prats JL. Clinical tests of paracetamol‐phenylbutazone combination [Ensayo clinico de la associacion paracetamol‐fenilbutazona]. Espanola de Reumatismo y Enfermedades Osteo‐Articulares 1968;12(8):233‐43. - PubMed
Lynch 2001 {published data only}
Maldykowa 1983 {published data only}
-
- Maldykowa H, Abgarowicz‐Milkowska T, Dratwianka B, Grabowska A, Jedryka A. Results of treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with Voltaren SR and Metindol [Wyniki leczenia voltarenem SR i metindolem chorych na reumatoidalne zapalenie stawow]. Reumatologia 1983;21(3‐4):265‐70. - PubMed
Maneksha 1973 {published data only}
-
- Maneksha S. 'Safapryn' and benorylate‐a comparative trial of two new preparations of aspirin and paracetamol in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Current Medical Research & Opinion 1973;1(9):563‐8. - PubMed
Mitchell 1984 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell H, Cunningham TJ, Mathews JD, Muirden KD. Further look at dextropropoxyphene with or without paracetamol in the treatment of arthritis. Medical Journal of Australia 1984;140(4):224‐5. - PubMed
Moll 1966 {published data only}
-
- Moll W. Therapeutic efficacy and tolerance of a combined phenylbutazone‐isopyrin preparation [Therapeutische Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit eines Phenylbutazon‐isopyrin‐kombinationspräparates]. Praxis 1966;55(49):1430‐5. - PubMed
Murphy 1978 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JE, Donald JF, Layes Molla A. Analgesic efficacy and acceptability of fenoprofen combined with paracetamol and compared with dihydrocodeine tartrate in general practice. Journal of International Medical Research 1978;6(5):375‐80. - PubMed
Pavelka 1972 {published data only}
-
- Pavelka K, Vojtisek O, Bremova A, Handlova D, Kankova D, Kralova M. Bufexamac in the treatment of progressive polyarthritis. Double‐blind test using phenylbutazone [Bufexamac v lécbe progresivni polyartritidy]. Casopis Lekaru Ceskych 1972;111(22):514‐7. - PubMed
Perrot 2006 {published data only}
-
- Perrot S, Maheu E, Javier R‐M, Eschalier A, Coutaux A, LeBars M, et al. Guidelines for the use of antidepressants in painful rheumatic conditions. European Journal of Pain 2006;10(3):185‐92. - PubMed
Raptopoulou 2008 {published data only}
-
- Raptopoulou A, Sidiropoulos P, Siakka P, Boki K, Drosos AA, Aslanidis S, et al. Evidence‐based recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis: results of the Hellenic working group of the 3E Initiative in Rheumatology. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2008;26(5):784‐92. - PubMed
Ridolfo 1982 {published data only}
-
- Ridolfo AS, Ashbrook EM, Schmid GE, Vogel JA, Rockhold FW, Offen WW. A double‐blind study comparing benoxaprofen, aspirin, and benoxaprofen plus aspirin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation 1982;5(2):239‐45. - PubMed
Robinson 1975 {published data only}
-
- Robinson H, Abruzzo JL, Miyara A, Ward JR. Concomitant tolmetin and aspirin therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Excerpta Medica 1975;10:102.
Roth 1975 {published data only}
-
- Roth SH, Englund DW, Harris BK, Ross HA. Tolmetin with acetaminophen in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Excerpta Medica 1975;1:112.
Rudge 1982 {published data only}
Sasisekhar 1973 {published data only}
-
- Sasisekhar PR, Penn RG, Haslock I, Wright V. A comparison of benorylate and aspirin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 1973;12(suppl):31‐8.
Sidiropoulos 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sidiropoulos PI, Hatemi G, Song IH, Avouac J, Collantes E, Hamuryudan V, et al. Evidence‐based recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis: systematic literature search of the 3E Initiative in Rheumatology involving a broad panel of experts and practising rheumatologists. Rheumatology 2008;47(3):355‐61. - PubMed
Torgyan 1979 {published data only}
-
- Torgyan S, Wagner L, Neumann T, Pakuts B, Csanyi M. A comparative study with indomethacin and combined indomethacin sodium‐salicylate in rheumatoid arthritis. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmacy 1979;17(11):439‐41. - PubMed
Triandaf 1970a {published data only}
-
- Triandaf I, Bobulesco V. Association of chlorzoxazone, acetaminophen and prednisolone (Predniflex) in the treatment of rheumatismal diseases [L'association de chlorzoxosone, acetaminophen et prednisolon (predniflex) dans le traitement des affections rhumatismales]. Revista Medico‐Chirurgicala a Societatii de Medici Si Naturalisti Din Iasi 1970;74(3):723‐7. - PubMed
Triandaf 1970b {published data only}
-
- Triandaf I, Bobulesco V. Clinical trial of an association of 5‐chlorobenzoxazolinone and N‐acetyl‐para‐aminophenol (Parafon) [Considerations sur léxpérimentation clinique d'une association entre le 5‐chlorobenzoxazolinone et le n‐acetyl‐para‐aminophenol (parafon)]. Revista Medico‐Chirurgicala a Societatii de Medici Si Naturalisti Din Iasi 1970;74(2):459‐63. - PubMed
Van Hoek 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hoek J. Trial of benorilate in rheumatic diseases [Benorylaast getoest in de rheumatologische practijk]. Ars Medici Internationaal Tijdschrift voor Praktische Therapie 1973;2(10):1739‐45.
Vergne‐Salle 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vergne‐Salle P, Mejjad O, Javier RM, Maheu E, Fallut M, Glowinski J, et al. Antiepileptic drugs to treat pain in rheumatic conditions. Recommendations based on evidence‐based review of the literature and expert opinion. Joint, Bone, Spine: Revue du Rheumatisme 2009;76(1):75‐85. - PubMed
Wettreich 1966 {published data only}
-
- Wettreich W. The association of paracetamol and phenylbutazone in rheumatology. Preliminary report [A associação paracetamol‐fenilbutazona em reumatologia]. Hospital 1966;70(2):427‐32. - PubMed
Willkens 1976 {published data only}
-
- Willkens RF, Segre EJ. Combination therapy with naproxen and aspirin in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1976;19(4):677‐82. - PubMed
Additional references
Atkins 2004
Bergman 2006
-
- Bergman MJ. Social and economic impact of inflammatory arthritis. Postgraduate Medicine 2006;Spec No:5‐11. - PubMed
Braun 1998
-
- Braun J, Bollow M, Remlinger G, Eggens U, Rudwaleit M, Distler A, et al. Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA‐B27 positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1998;41(1):58‐67. - PubMed
Calin 1994
-
- Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O'Hea J, Mallorie P, et al. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21(12):2281‐5. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988.
Da Silva 2010
-
- Silva JA, Ramiro S, Pedro S, Rodrigues A, Vasconcelos JC, Benito‐Garcia E. Patients and physicians priorities for improvement. The case of rheumatic diseases. Acta Reumatologica Portuguesa 2010;35(2):192‐9. - PubMed
De Angelis 2004
-
- Angelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, Haug C, Hoey J, Horton R, et al. Clinical trial registration: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. JAMA 2004;292(11):1363‐4. - PubMed
De Jong 1997
-
- Jong Z, Heijde D, McKenna SP, Whalley D. The reliability and construct validity of the RAQoL: a rheumatoid arthritis‐specific quality of life instrument. British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36(8):878‐83. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Dougados 2011
-
- Dougados M, Simon P, Braun J, Burgos‐Vargas R, Maksymowych WP, Sieper J, et al. ASAS recommendations for collecting, analysing and reporting NSAID intake in clinical trials/epidemiological studies in axial spondyloarthritis. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 2011;70(2):249‐51. - PubMed
Doward 2003
Finnerup 2010
-
- Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010;150(3):573‐81. - PubMed
Fries 1980
-
- Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1980;23(2):137‐45. - PubMed
Gabriel 2001
-
- Gabriel SE. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatic Disease Clinics 2001;27(2):269‐81. - PubMed
Heiberg 2002
-
- Heiberg T, Kvien TK. Preferences for improved health examined in 1,024 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pain has highest priority. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47(4):391‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kasis 1983
-
- Kazis LE, Meenan RF, Anderson JJ. Pain in the rheumatic diseases. Investigation of a key health status component. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1983;26(8):1017‐22. - PubMed
Keystone 2004
-
- Keystone EC, Kavanaugh AF, Sharp JT, Tannenbaum H, Hua Y, Teoh LS, et al. Radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti‐tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy: a randomized, placebo‐controlled, 52‐week trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;50(5):1400‐11. - PubMed
Kvien 2004
-
- Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):1‐12. - PubMed
Lanser 2001
-
- Lanser P, Gesell S. Pain management: the fifth vital sign. Health Benchmarks 2001;8(6):68‐70. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Mease 2000
-
- Mease PJ, Goffe BS, Metz J, VanderStoep A, Finck B, Burge DJ. Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet 2000;356(9227):385‐90. - PubMed
Minnock 2003
-
- Minnock P, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B. Quality of life, social support, and knowledge of disease in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;49(2):221‐7. - PubMed
Moore 2010
-
- Moore AR, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain‐ establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. - PubMed
Peto 1976
Philips 2000
-
- Phillips DM. JCAHO pain management standards are unveiled. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. JAMA 2000;284(4):428‐9. - PubMed
Pincus 1983
-
- Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1983;26(11):1346‐53. - PubMed
Ramiro 2010
-
- Ramiro S, Radner H, Heijde D, Tubergen A, Buchbinder R, Aletaha D, et al. Combination therapy for pain management in inflammatory arthritis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008886] - DOI
Saarto 2007
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Skevington 1998
-
- Skevington SM. Investigating the relationship between pain and discomfort and quality of life, using the WHOQOL. Pain 1998;76(3):395‐406. - PubMed
Smolen 2010a
Smolen 2010b
Ten Klooster 2007
Van der Heijde 2005
-
- Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, Sieper J, DeWoody K, Williamson P, et al. Ankylosing Spondylitis Study for the Evaluation of Recombinant Infliximab Therapy Study Group. Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial (ASSERT). Arthritis and Rheumatism 2005;52(2):582‐91. - PubMed
Ware 2001
-
- Ware JE, Kosinski M. SF‐36 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales: manual for users version 1. 2nd Edition. Lincoln, Rhode Island, USA: Quality Metric, 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous