Rapid loss of dendritic HCN channel expression in hippocampal pyramidal neurons following status epilepticus
- PMID: 21976514
- PMCID: PMC3208968
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1148-11.2011
Rapid loss of dendritic HCN channel expression in hippocampal pyramidal neurons following status epilepticus
Abstract
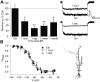
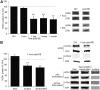
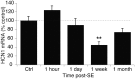
Epilepsy is associated with loss of expression and function of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) ion channels. Previously, we showed that loss of HCN channel-mediated current (I(h)) occurred in the dendrites of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (SE), accompanied by loss of HCN1 channel protein expression. However, the precise onset and mechanistic basis of HCN1 channel loss post-SE was unclear, particularly whether it preceded the onset of spontaneous recurrent seizures and could contribute to epileptogenesis or development of the epileptic state. Here, we found that loss of I(h) and HCN1 channel expression began within an hour after SE and involved sequential processes of dendritic HCN1 channel internalization, delayed loss of protein expression, and later downregulation of mRNA expression. We also found that an in vitro SE model reproduced the rapid loss of dendritic I(h), demonstrating that this phenomenon was not specific to in vivo SE. Together, these results show that HCN1 channelopathy begins rapidly and persists after SE, involves both transcriptional and nontranscriptional mechanisms, and may be an early contributor to epileptogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Bernard C, Anderson A, Becker A, Poolos NP, Beck H, Johnston D. Acquired dendritic channelopathy in temporal lobe epilepsy. Science. 2004;305:532–535. - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Kayal AR, Shumate MD, Jin H, Rikhter TY, Coulter DA. Selective changes in single cell GABAA receptor subunit expression and function in temporal lobe epilepsy. Nat Med. 1998;4:1166–1172. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Larionov S, Pitsch J, Hoerold N, Ullmann C, Elger CE, Schramm J, Becker AJ. Expression analysis of metabotropic glutamate receptors I and III in mouse strains with different susceptibility to experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Lett. 2005;375:192–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
