Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy using genetically engineered antibody-streptavidin fusion proteins for treatment of non-hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 21976541
- PMCID: PMC3229652
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1204
Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy using genetically engineered antibody-streptavidin fusion proteins for treatment of non-hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy (PRIT) using streptavidin (SAv)-biotin technology can deliver higher therapeutic doses of radioactivity to tumors than conventional RIT. However, "endogenous" biotin can interfere with the effectiveness of this approach by blocking binding of radiolabeled biotin to SAv. We engineered a series of SAv FPs that downmodulate the affinity of SAv for biotin, while retaining high avidity for divalent DOTA-bis-biotin to circumvent this problem.
Experimental design: The single-chain variable region gene of the murine 1F5 anti-CD20 antibody was fused to the wild-type (WT) SAv gene and to mutant SAv genes, Y43A-SAv and S45A-SAv. FPs were expressed, purified, and compared in studies using athymic mice bearing Ramos lymphoma xenografts.
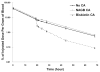
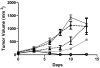
Results: Biodistribution studies showed delivery of more radioactivity to tumors of mice pretargeted with mutant SAv FPs followed by (111)In-DOTA-bis-biotin [6.2 ± 1.7% of the injected dose per gram (%ID/gm) of tumor 24 hours after Y43A-SAv FP and 5.6 ± 2.2%ID/g with S45A-SAv FP] than in mice on normal diets pretargeted with WT-SAv FP (2.5 ± 1.6%ID/g; P = 0.01). These superior biodistributions translated into superior antitumor efficacy in mice treated with mutant FPs and (90)Y-DOTA-bis-biotin [tumor volumes after 11 days: 237 ± 66 mm(3) with Y43A-SAv, 543 ± 320 mm(3) with S45A-SAv, 1129 ± 322 mm(3) with WT-SAv, and 1435 ± 212 mm(3) with control FP (P < 0.0001)].
Conclusions: Genetically engineered mutant-SAv FPs and bis-biotin reagents provide an attractive alternative to current SAv-biotin PRIT methods in settings where endogenous biotin levels are high.
©2011 AACR.
Figures



References
-
- Vose JM. Current approaches to the management of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Semin Oncol. 1998 Aug;25(4):483–91. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI, Gaynor ER, Dahlberg S, Oken MM, Grogan TM, Mize EM, et al. Comparison of a standard regimen (CHOP) with three intensive chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Apr 8;328(14):1002–6. - PubMed
-
- Horning SJ. Treatment approaches to the low-grade lymphomas. Blood. 1994 Feb 15;83(4):881–4. - PubMed
-
- Kaminski MS, Zelenetz AD, Press OW, Saleh M, Leonard J, Fehrenbacher L, et al. Pivotal study of iodine I 131 tositumomab for chemotherapy-refractory low-grade or transformed low-grade B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 2001 Oct 1;19(19):3918–28. - PubMed
-
- Knox SJ, Goris ML, Trisler K, Negrin R, Davis T, Liles TM, et al. Yttrium-90-labeled anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy of recurrent B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Mar 2;(3):457–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

