Serratia infections: from military experiments to current practice
- PMID: 21976608
- PMCID: PMC3194826
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00017-11
Serratia infections: from military experiments to current practice
Abstract
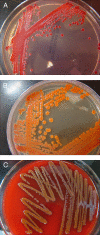
Serratia species, in particular Serratia marcescens, are significant human pathogens. S. marcescens has a long and interesting taxonomic, medical experimentation, military experimentation, and human clinical infection history. The organisms in this genus, particularly S. marcescens, were long thought to be nonpathogenic. Because S. marcescens was thought to be a nonpathogen and is usually red pigmented, the U.S. military conducted experiments that attempted to ascertain the spread of this organism released over large areas. In the process, members of both the public and the military were exposed to S. marcescens, and this was uncovered by the press in the 1970s, leading to U.S. congressional hearings. S. marcescens was found to be a certain human pathogen by the mid-1960s. S. marcescens and S. liquefaciens have been isolated as causative agents of numerous outbreaks and opportunistic infections, and the association of these organisms with point sources such as medical devices and various solutions given to hospitalized patients is striking. Serratia species appear to be common environmental organisms, and this helps to explain the large number of nosocomial infections due to these bacteria. Since many nosocomial infections are caused by multiply antibiotic-resistant strains of S. marcescens, this increases the danger to hospitalized patients, and hospital personnel should be vigilant in preventing nosocomial outbreaks due to this organism. S. marcescens, and probably other species in the genus, carries several antibiotic resistance determinants and is also capable of acquiring resistance genes. S. marcescens and S. liquefaciens are usually identified well in the clinical laboratory, but the other species are rare enough that laboratory technologists may not recognize them. 16S rRNA gene sequencing may enable better identification of some of the less common Serratia species.
Figures
References
-
- Aïtoff M., Dion M., Dobkevitch H. 1936. Bacillus prodigiosus pathogène pour les animoux: endotoxine et reaction de Shwartzman. C. R. Soc. Biol. 123:375–376(In French.)
-
- Ajithkumar B., Ajithkumar V. P., Iriye R., Doi Y., Sakai T. 2003. Spore-forming Serratia marcescens subsp. sakuensis subsp. nov., isolated from a domestic wastewater treatment tank. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53:253–258 - PubMed
-
- Alexandrakis G., Alfonso E. C., Miller D. 2000. Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in south Florida and emerging resistance to fluoroquinolones. Ophthalmology 107:1497–1502 - PubMed
-
- Al Jarousha A. M., El Qouqa I. A., El Jadba A. H. N., Al Afifi A. S. 2008. An outbreak of Serratia marcescens septicaemia in neonatal intensive care unit in Gaza City, Palestine. J. Hosp. Infect. 70:119–126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

