Staphylococcus haemolyticus as an important hospital pathogen and carrier of methicillin resistance genes
- PMID: 21976766
- PMCID: PMC3256717
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05563-11
Staphylococcus haemolyticus as an important hospital pathogen and carrier of methicillin resistance genes
Abstract
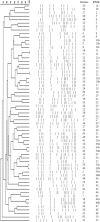
Phenotypic and molecular methods were used to characterize the antibiotic resistance of 64 clinical isolates of Staphylococcus haemolyticus. By PCR of the mecA gene, 87% were found to be methicillin resistant. Approximately 55% harbored staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec element (SCCmec) type V, and only one SCCmec type IV. Many isolates (75%) displayed multiresistance, and pulsotype analysis showed a high diversity.
Figures
References
-
- Berglund C, Söderquist B. 2008. The origin of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate at a neonatal ward in Sweden—possible horizontal transfer of a staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec between methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 14:1048–1056 - PubMed
-
- Caierão J, et al. 2004. Evaluation of phenotypic methods for methicillin resistance characterization in coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS). J. Med. Microbiol. 53:1195–1199 - PubMed
-
- Chiew YF, et al. 2007. Detection of vancomycin heteroresistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus and vancomycin intermediate resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis by means of vancomycin screening agar. Pathology 39:375–377 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2010. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. CLSI document M100-S20. CLSI, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical