Histomorphometric and sympathetic innervation of the human renal artery: A cadaveric study
- PMID: 21976927
- PMCID: PMC3183706
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-7796.84968
Histomorphometric and sympathetic innervation of the human renal artery: A cadaveric study
Abstract
Background and aim: Renal artery stenosis (RAS) and acute renal failure may be due to the intimal hyperplasia and sympathetic fibers of the renal artery (RA), respectively. The purpose of this study was to characterize arterial wall and sympathetic innervation of the human RA.
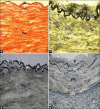
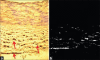
Materials and methods: Fifty-two fresh human RA samples (proximal part) were collected from 26 cadavers (19 males and 7 females), between the ages of 19 and 83 years, during autopsy. Samples were divided into three age groups: Group 1, 19-40 years; Group 2, 41-60 years; Group 3, over 61 years. 5-μm thick sections of each sample were taken and stained with hematoxylin-eosin and Verhoeff-Van Gieson. Five out of 52 samples were processed for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunostaining.
Results: Our histological studies revealed that tunica media of RA showed smooth muscle cells and fine irregularly arranged elastic fibers. Intimal hyperplasia was the most common finding. The present study showed that thickness of tunica intima and media were found to increase with age. Sympathetic nerves were present in the tunica adventitia and outer media of the RA. The mean adventitial and sympathetic nerve fiber areas were found to be 0.595 and 0.071 mm(2), respectively. Sympathetic index (SI) to RA was calculated by dividing the sympathetic fiber area by the adventitial area of the RA. SI of RA was found to be 0.140.
Conclusion: We conclude that RA showed the structure of musculo-elastic artery. SI may be used for the analysis of sympathetic fiber related problems of the human RA or kidneys.
Keywords: Histology; intimal hyperplasia; stenosis; sympathetic nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Yamaguchi T, Omae T, Katsuki S. Quantitative determination of renal vascular changes related to age and hypertension. Jpn Heart J. 1969;10:248–58. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal A, Kapoor K, Singh B. Prevalence and severity of atherosclerosis in renal artery in Northwest Indian population: An autopsy study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2009;31:349–56. - PubMed

