Ketamine inhibits lung fluid clearance through reducing alveolar sodium transport
- PMID: 21976965
- PMCID: PMC3185271
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/460596
Ketamine inhibits lung fluid clearance through reducing alveolar sodium transport
Abstract
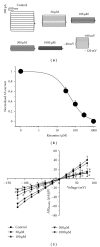
Ketamine is a broadly used anaesthetic for analgosedation. Accumulating clinical evidence shows that ketamine causes pulmonary edema with unknown mechanisms. We measured the effects of ketamine on alveolar fluid clearance in human lung lobes ex vivo. Our results showed that intratracheal instillation of ketamine markedly decreased the reabsorption of 5% bovine serum albumin instillate. In the presence of amiloride (a specific ENaC blocker), fluid resolution was not further decreased, suggesting that ketamine could decrease amiloride-sensitive fraction of AFC associated with ENaC. Moreover, we measured the regulation of amiloride-sensitive currents by ketamine in A549 cells using whole-cell patch clamp mode. Our results suggested that ketamine decreased amiloride-sensitive Na+ currents (ENaC activity) in a dose-dependent fashion. These data demonstrate that reduction in lung ENaC activity and lung fluid clearance following administration of ketamine may be the crucial step of the pathogenesis of resultant pulmonary edema.
Figures

References
-
- Pandey CK, Mathur N, Singh N, Chandola HC. Fulminant pulmonary edema after intramuscular ketamine. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia. 2000;47(9):894–896. - PubMed
-
- Murphy JL., Jr. Hypertension and pulmonary oedema associated with ketamine administration in a patient with a history of substance abuse. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia. 1993;40(2):160–164. - PubMed
-
- Boutureira J, Trim CM, Cornell KK. Acute pulmonary edema after diazepam-ketamine in a dog. Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia. 2007;34(5):371–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

