Cardiac insulin resistance and microRNA modulators
- PMID: 21977024
- PMCID: PMC3184440
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/654904
Cardiac insulin resistance and microRNA modulators
Abstract
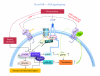
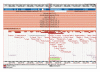
Cardiac insulin resistance is a metabolic and functional disorder that is often associated with obesity and/or the cardiorenal metabolic syndrome (CRS), and this disorder may be accentuated by chronic alcohol consumption. In conditions of over-nutrition, increased insulin (INS) and angiotensin II (Ang II) activate mammalian target for rapamycin (mTOR)/p70 S6 kinase (S6K1) signaling, whereas chronic alcohol consumption inhibits mTOR/S6K1 activation in cardiac tissue. Although excessive activation of mTOR/S6K1 induces cardiac INS resistance via serine phosphorylation of INS receptor substrates (IRS-1/2), it also renders cardioprotection via increased Ang II receptor 2 (AT2R) upregulation and adaptive hypertrophy. In the INS-resistant and hyperinsulinemic Zucker obese (ZO) rat, a rodent model for CRS, activation of mTOR/S6K1signaling in cardiac tissue is regulated by protective feed-back mechanisms involving mTOR↔AT2R signaling loop and profile changes of microRNA that target S6K1. Such regulation may play a role in attenuating progressive heart failure. Conversely, alcohol-mediated inhibition of mTOR/S6K1, down-regulation of INS receptor and growth-inhibitory mir-200 family, and upregulation of mir-212 that promotes fetal gene program may exacerbate CRS-related cardiomyopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Sowers JR. Hypertension, angiotensin II, and oxidative stress. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;346(25):1999–2001. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR. Metabolic risk factors and renal disease. Kidney International. 2007;71(8):719–720. - PubMed
-
- Galassi A, Reynolds K, He J. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis. American Journal of Medicine. 2006;119(10):812–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
