Antimyeloma Effects of the Heat Shock Protein 70 Molecular Chaperone Inhibitor MAL3-101
- PMID: 21977030
- PMCID: PMC3184436
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/232037
Antimyeloma Effects of the Heat Shock Protein 70 Molecular Chaperone Inhibitor MAL3-101
Abstract
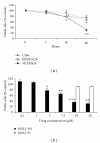
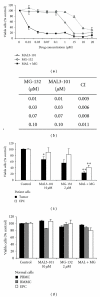
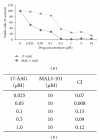
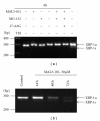
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematologic malignancy and remains incurable, primarily due to the treatment-refractory/resistant nature of the disease. A rational approach to this compelling challenge is to develop new drugs that act synergistically with existing effective agents. This approach will reduce drug concentrations, avoid treatment resistance, and also improve treatment effectiveness by targeting new and nonredundant pathways in MM. Toward this goal, we examined the antimyeloma effects of MAL3-101, a member of a new class of non-ATP-site inhibitors of the heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 molecular chaperone. We discovered that MAL3-101 exhibited antimyeloma effects on MM cell lines in vitro and in vivo in a xenograft plasmacytoma model, as well as on primary tumor cells and bone marrow endothelial cells from myeloma patients. In combination with a proteasome inhibitor, MAL3-101 significantly potentiated the in vitro and in vivo antimyeloma effects. These data support a preclinical rationale for small molecule inhibition of Hsp70 function, either alone or in combination with other agents, as an effective therapeutic strategy for MM.
Figures


References
-
- Fewell SW, Smith CM, Lyon MA, et al. Small molecule modulators of endogenous and co-chaperone-stimulated Hsp70 ATPase activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(49):51131–51140. - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma: 2011 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. American Journal of Hematology. 2011;86(1):57–65. - PubMed
-
- Barlogie B, Kyle RA, Anderson KC, et al. Standard chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemoradiotherapy for multiple myeloma: final results of phase III US intergroup trial S9321. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24(6):929–936. - PubMed
-
- Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM. Molecular pathogenesis and a consequent classification of multiple myeloma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(26):6333–6338. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

