Total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy - a radiological evaluation
- PMID: 21977186
- PMCID: PMC3150017
Total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy - a radiological evaluation
Abstract
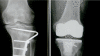
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the results of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) following a closed wedge high tibial osteotomy (HTO). A total of 16 TKAs were performed in 16 pacients who had previously undergone a closed wedge (HTO) as a treatement for knee osteoarthritis. The radiographic results were evaluated with respect to the femurotibial angle (FTA), joint line height (JLH), tibial bone resection and Insall-Salvati ratio. The FTA improved in average, from 6.5 degree of varus preoperatively at 5.7 degree of valgus postoperatively. The JLH averaged 14.34 mm preop and 13.81 mm at the last follow-up. The amount of tibial bone resection averaged 5.98 mm, face to 7.5 mm for knees without HTO. The Insall-Salvati ratio was 1.127 preop and 1.172 postop. A meticulous surgical technique may lead to satisfactory results in TKA after HTO, considering the correction of the deformity, the re-estabilish of JLH and the amount of the tibial bone resection.
Keywords: knee arthroplasty; radiological evaluation; tibial osteotomy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Total knee arthroplasty following closed wedge high tibial osteotomy.Int Orthop. 2010 Feb;34(2):283-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0749-6. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Int Orthop. 2010. PMID: 19367405 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of mid-term results between conversion total knee arthroplasties following closed wedge high tibial osteotomy and primary total knee arthroplasties: A matched pair study including patellar symptom and position.J Orthop Sci. 2017 May;22(3):495-500. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2016.12.019. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Orthop Sci. 2017. PMID: 28100411
-
Computer Navigation Technique for Simultaneous Total Knee Arthroplasty and Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in Patients with Large Tibial Varus Deformity.Surg Technol Int. 2020 Nov 28;37:265-274. Surg Technol Int. 2020. PMID: 33238026
-
Conversion Total Knee Arthroplasty after Failed High Tibial Osteotomy.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016 Jun;28(2):89-98. doi: 10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.2.89. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 27274465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Changes of patella position after closed and open wedge high tibial osteotomy: review of the literature].Orthopade. 2012 Mar;41(3):186, 188-94. doi: 10.1007/s00132-011-1872-9. Orthopade. 2012. PMID: 22407093 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Comparison of radiological features of high tibial osteotomy and tibial condylar valgus osteotomy.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Sep 4;20(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2764-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31484580 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of short-term clinical outcomes between open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and tibial condylar valgus osteotomy.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jan 27;25(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07205-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38281004 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy.Indian J Orthop. 2013 Sep;47(5):469-73. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.118202. Indian J Orthop. 2013. PMID: 24133306 Free PMC article.
-
Tibial condylar valgus osteotomy for the treatment of intra-articular varus deformity of the knee.Ann Jt. 2022 Oct 15;7:37. doi: 10.21037/aoj-22-19. eCollection 2022. Ann Jt. 2022. PMID: 38529161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total knee arthroplasty after failed high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review of open versus closed wedge osteotomy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Aug;24(8):2567-77. doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3807-1. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. PMID: 26423055
References
-
- Odenbring S, Egund N, Hagstedt B, et al. Ten-year results of tibial osteotomy for medial gonarthrosis: the influence of overcorrection. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;110:103–103. - PubMed
-
- Hunt MA, Birmingham TB, Bryant D, et al. Lateral trunk lean explains variation in dynamic knee joint load in patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:591–9. - PubMed
-
- Mundermann A, Dyrby CO, Hurwitz DE. Potential strategies to reduce medial compartment loading in patients with knee osteoarthritis of varying severity: reduced walking speed. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1172–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
