Ventricular arrhythmias in competitive athletes: risk stratification with T-wave alternans
- PMID: 21977276
- PMCID: PMC3184678
- DOI: 10.4081/hi.2007.58
Ventricular arrhythmias in competitive athletes: risk stratification with T-wave alternans
Abstract
Introduction: Aim of our study is to evaluate the role of TWA to stratify the risk of sudden cardiac death in athletes (Ath) with complex ventricular arrhythmias (VA), and to document a possible correlation between TWA and electrophysiological testing (EES) results.
Methods: We studied 43 Ath with VA (31 M, mean age 34 ± 12 years). In all cases a cardiological evaluation was performed, including TWA and EES. The patients were evaluated during a follow-up of 25 ± 22 months. The end-point was the occurrence of sudden death or malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias (VT).
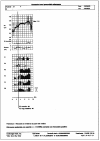
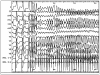
Results: TWA was negative in 28 Ath (65%), positive in 8 (19%) and indeterminate in 7 (16%). All subjects with negative TWA did not show induction of VT at EES, with significant correlation between negative TWA and negative EES (p<0.001). All Ath with positive TWA also had VT induced by a EES, but without significant correlation between positive TWA and positive EES. In 2 Ath with undetermined TWA (29%) VT were induced at EES. Our data did not show significant correlation between indeterminate TWA and positive or negative EES. However, logistic regression analysis showed significant correlation between abnormal TWA test (positive or indeterminate) and inducibility of VT at EES (p<0.001). During follow-up we observed a significant difference in end-point occurrence between Ath with negative or positive TWA and between Ath with negative or positive EES.
Conclusion: TWA confirm its role as a simple and non-invasive test, and it seems useful for prognostic stratification of Ath with VA.
Keywords: Sport activity; Sudden death; T-wave alternans; Ventricular arrhythmias.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Microvolt T-wave alternans for risk stratification in athletes with ventricular arrhythmias: correlation with programmed ventricular stimulation.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008 Jan;13(1):14-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2007.00196.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008. PMID: 18234002 Free PMC article.
-
Microvolt T-wave alternans as predictor of electrophysiological testing results in professional competitive athletes.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004 Jul;9(3):201-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2004.93543.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004. PMID: 15245334 Free PMC article.
-
Microvolt T-wave alternans for the risk stratification of dangerous ventricular arrhythmias in patients with previously implanted automatic cardioverter-defibrillator.Kardiol Pol. 2011;69(6):580-5. Kardiol Pol. 2011. PMID: 21678296
-
Repolarization alternans: implications for the mechanism and prevention of sudden cardiac death.Cardiovasc Res. 2003 Mar;57(3):599-614. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00737-x. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12618222 Review.
-
[T-wave alternans in microwave frequency as a new indicator of disordered ventricular repolarization: pathophysiology, methodology, clinical results].Z Kardiol. 1999 Dec;88(12):974-81. doi: 10.1007/s003920050379. Z Kardiol. 1999. PMID: 10654388 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Heart of the World's Top Ultramarathon Runner-Not Necessarily Much Different from Normal.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Jan 28;10(2):73. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10020073. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32012817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corrado D, Basso C, Rizzoli G, Schiavon M, Tiene G. Does sports activity enhance the risk of sudden death in adolescents and young adults? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1959–63. - PubMed
-
- Adam D, Smith J, Askelrod S, et al. Fluctuations in T-wave morphology and susceptibility to ventricular fibrillation. J Electrocardiol. 1984;17:209–18. - PubMed
-
- Smith JM, Clancy EA, Valeri R, Ruskin JN, Cohen RJ. Electrical alternans and cardiac electrical instability. Circulation. 1988;77:110–21. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum DS, Jackson LE, Smith JM, et al. Electrical alternans and vulnerability to ventricular arrhythmias. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:235–41. - PubMed
-
- Nearing B, Huang AH, Verrier RL. Dynamic tracking of cardiac vulnerability by complex demodulation of the T-wave. Science. 1991;252:437–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
