The prognostic value of the nodal ratio in N1 breast cancer
- PMID: 21978463
- PMCID: PMC3198692
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-131
The prognostic value of the nodal ratio in N1 breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Although the nodal ratio (NR) has been recognized as a prognostic factor in breast cancer, its clinical implication in patients with 1-3 positive nodes (N1) remains unclear. Here, we evaluated the prognostic value of the NR and identified other clinico-pathologic variables associated with poor prognosis in these patients.
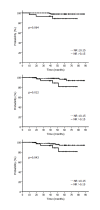
Methods: We analyzed 130 patients with N1 invasive breast cancer who were treated at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital from March 2003 to December 2007. Disease-free survival (DFS), locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRRFS), and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) were compared according to the NR with a cut-off value of 0.15.
Results: We followed patients' recovery for a median duration of 59 months. An NR > 0.15 was found in 23.1% of patients, and a median of 18 nodes were dissected per patient (range 1-59). The NR was statistically independent from other prognostic variables, such as patient age, T stage, extent of surgery, pathologic factors in the chi square test. On univariate analysis, patients with a NR > 0.15 had significantly lower 5-year LRRFS (88.7% vs. 97.9%, p = 0.033) and 5-year DMFS (81.3% vs. 96.4%, p = 0.029) and marginally lower 5-year DFS (81.3% vs. 94.0%, p = 0.069) than those with a NR ≤0.15, respectively. Since the predictive power of the NR was found to differ with diverse clinical and pathologic variables, we performed adjusted analysis stratified by age, pathologic characteristics, and adjuvant treatments. Only young patients with a NR > 0.15 showed significantly lower DFS (p = 0.027) as well as those presenting an unfavorable pathologic profile such as advanced T stage (p = 0.034), histologic grade 3 (p = 0.034), positive lymphovascular invasion (p = 0.037), involved resection margin (p = 0.007), and no chemotherapy (p = 0.014) or regional radiotherapy treatment (p = 0.039). On multivariate analysis, a NR > 0.15 was significantly associated with lower DFS (p = 0.043) and DMFS (p = 0.012), but not LRRFS (p = 0.064).
Conclusions: A NR > 0.15 was associated with an increased risk of recurrence, especially in young patients with unfavorable pathologic profiles.
Figures

References
-
- Vinh-Hung V, Burzykowski T, Cserni G, Voordeckers M, Van De Steene J, Storme G. Functional form of the effect of the numbers of axillary nodes on survival in early breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2003;22:697–704. - PubMed
-
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7. New York: Springer; 2010. Chapter 32. Breast; pp. 347–369.
-
- Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, Robinson DS, Estabrook A, Fine RE, Fleming GF, Formenti S, Hudis C, Kirshner JJ, Krause DA, Kuske RR, Langer AS, Sledge GW Jr, Whelan TJ, Pfister DG. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: Clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1539–1569. - PubMed
-
- Truong PT, Berthelet E, Lee J, Kader HA, Olivotto IA. The prognostic significance of the percentage of positive/dissected axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer recurrence and survival in patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes. Cancer. 2005;103:2006–2014. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20969. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

