Genomic phenotyping of the essential and non-essential yeast genome detects novel pathways for alkylation resistance
- PMID: 21978764
- PMCID: PMC3213080
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-157
Genomic phenotyping of the essential and non-essential yeast genome detects novel pathways for alkylation resistance
Abstract
Background: A myriad of new chemicals has been introduced into our environment and exposure to these agents can damage cells and induce cytotoxicity through different mechanisms, including damaging DNA directly. Analysis of global transcriptional and phenotypic responses in the yeast S. cerevisiae provides means to identify pathways of damage recovery upon toxic exposure.
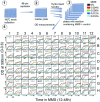
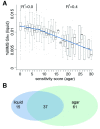
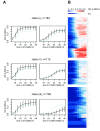
Results: Here we present a phenotypic screen of S. cerevisiae in liquid culture in a microtiter format. Detailed growth measurements were analyzed to reveal effects on ~5,500 different haploid strains that have either non-essential genes deleted or essential genes modified to generate unstable transcripts. The pattern of yeast mutants that are growth-inhibited (compared to WT cells) reveals the mechanisms ordinarily used to recover after damage. In addition to identifying previously-described DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint deficient strains, we also identified new functional groups that profoundly affect MMS sensitivity, including RNA processing and telomere maintenance.
Conclusions: We present here a data-driven method to reveal modes of toxicity of different agents that impair cellular growth. The results from this study complement previous genomic phenotyping studies as we have expanded the data to include essential genes and to provide detailed mutant growth analysis for each individual strain. This eukaryotic testing system could potentially be used to screen compounds for toxicity, to identify mechanisms of toxicity, and to reduce the need for animal testing.
Figures


References
-
- Begley TJ, Rosenbach AS, Ideker T, Samson LD. Damage recovery pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic phenotyping and interactome mapping. Molecular Cancer Research. 2002;1(2):103–112. - PubMed
-
- Begley TJ, Rosenbach AS, Ideker T, Samson LD. Hot spots for modulating toxicity identified by genomic phenotyping and localization mapping. Molecular Cell. 2004;16(1):117–125. - PubMed
-
- Jelinsky SA, Estep P, Church GM, Samson LD. Regulatory networks revealed by transcriptional profiling of damaged Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells: Rpn4 links base excision repair with proteasomes. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2000;20(21):8157–8167. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8157-8167.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang M, Bellaoui M, Boone C, Brown GW. A genome-wide screen for methyl methanesulfonate-sensitive mutants reveals genes required for S phase progression in the presence of DNA damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99(26):16934–16939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.262669299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

