Identifying bilingual semantic neural representations across languages
- PMID: 21978845
- PMCID: PMC4620940
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandl.2011.09.003
Identifying bilingual semantic neural representations across languages
Abstract
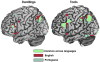
The goal of the study was to identify the neural representation of a noun's meaning in one language based on the neural representation of that same noun in another language. Machine learning methods were used to train classifiers to identify which individual noun bilingual participants were thinking about in one language based solely on their brain activation in the other language. The study shows reliable (p<.05) pattern-based classification accuracies for the classification of brain activity for nouns across languages. It also shows that the stable voxels used to classify the brain activation were located in areas associated with encoding information about semantic dimensions of the words in the study. The identification of the semantic trace of individual nouns from the pattern of cortical activity demonstrates the existence of a multi-voxel pattern of activation across the cortex for a single noun common to both languages in bilinguals.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Barsalou LW. Perceptual symbol systems. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 1999;22:577–660. - PubMed
-
- Caramazza A, Brones I. Semantic classification by bilinguals. Canadian Journal of Psychology/Revue Canadienne de Psychologie. 1980;34(1):77–81.
-
- Chen HC, Ho C. Development of Stroop interference in Chinese-English bilinguals. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 1986;12:397–401.
-
- Cox DD, Savoy RL. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) “brain reading”: Detecting and classifying distributed patterns of fMRI activity in human visual cortex. Neuroimage. 2003;19:261–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

