Control of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by NF-κB promotes senescence and enhances chemosensitivity
- PMID: 21979375
- PMCID: PMC3205583
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.17276711
Control of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by NF-κB promotes senescence and enhances chemosensitivity
Abstract
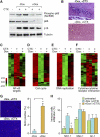
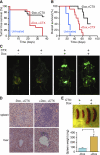
Cellular senescence acts as a potent barrier to tumorigenesis and contributes to the anti-tumor activity of certain chemotherapeutic agents. Senescent cells undergo a stable cell cycle arrest controlled by RB and p53 and, in addition, display a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) involving the production of factors that reinforce the senescence arrest, alter the microenvironment, and trigger immune surveillance of the senescent cells. Through a proteomics analysis of senescent chromatin, we identified the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) subunit p65 as a major transcription factor that accumulates on chromatin of senescent cells. We found that NF-κB acts as a master regulator of the SASP, influencing the expression of more genes than RB and p53 combined. In cultured fibroblasts, NF-κB suppression causes escape from immune recognition by natural killer (NK) cells and cooperates with p53 inactivation to bypass senescence. In a mouse lymphoma model, NF-κB inhibition bypasses treatment-induced senescence, producing drug resistance, early relapse, and reduced survival. Our results demonstrate that NF-κB controls both cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous aspects of the senescence program and identify a tumor-suppressive function of NF-κB that contributes to the outcome of cancer therapy.
Figures
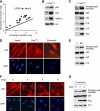
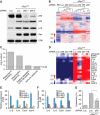
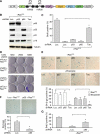
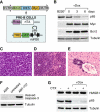
Comment in
-
Senescence. NF-κB shows its beneficial side.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 Oct 28;11(12):832-3. doi: 10.1038/nrc3168. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22020169 No abstract available.
References
-
- Acosta JC, O'Loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N, et al. 2008. Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133: 1006–1018 - PubMed
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS 2006. Nuclear factor-κB and inhibitor of κB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25: 6817–6830 - PubMed
-
- Campisi J 2005. Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120: 513–522 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R43 RR021239/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008444/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA143177/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR021239/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R41 CA122715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA122715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R42 CA122715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA143177/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG16379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R44 RR021239/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG016379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
