TRAP1 and the proteasome regulatory particle TBP7/Rpt3 interact in the endoplasmic reticulum and control cellular ubiquitination of specific mitochondrial proteins
- PMID: 21979464
- PMCID: PMC3307973
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.128
TRAP1 and the proteasome regulatory particle TBP7/Rpt3 interact in the endoplasmic reticulum and control cellular ubiquitination of specific mitochondrial proteins
Abstract
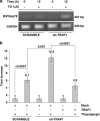
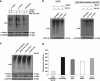
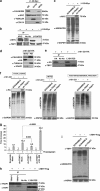
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein-1 (TRAP1) is a mitochondrial (MITO) antiapoptotic heat-shock protein. The information available on the TRAP1 pathway describes just a few well-characterized functions of this protein in mitochondria. However, our group's use of mass-spectrometric analysis identified TBP7, an AAA-ATPase of the 19S proteasomal subunit, as a putative TRAP1-interacting protein. Surprisingly, TRAP1 and TBP7 colocalize in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), as demonstrated by biochemical and confocal/electron microscopic analyses, and interact directly, as confirmed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis. This is the first demonstration of TRAP1's presence in this cellular compartment. TRAP1 silencing by short-hairpin RNAs, in cells exposed to thapsigargin-induced ER stress, correlates with upregulation of BiP/Grp78, thus suggesting a role of TRAP1 in the refolding of damaged proteins and in ER stress protection. Consistently, TRAP1 and/or TBP7 interference enhanced stress-induced cell death and increased intracellular protein ubiquitination. These experiments led us to hypothesize an involvement of TRAP1 in protein quality control for mistargeted/misfolded mitochondria-destined proteins, through interaction with the regulatory proteasome protein TBP7. Remarkably, expression of specific MITO proteins decreased upon TRAP1 interference as a consequence of increased ubiquitination. The proposed TRAP1 network has an impact in vivo, as it is conserved in human colorectal cancers, is controlled by ER-localized TRAP1 interacting with TBP7 and provides a novel model of the ER-mitochondria crosstalk.
Figures




References
-
- Song HY, Dunbar JD, Zhang YX, Guo D, Donner DB. Identification of a protein with homology to HSP90 that binds the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:3574–3581. - PubMed
-
- Felts SJ, Owen BA, Nguyen P, Trepel J, Donner DB, Toft DO. The HSP90-related protein TRAP1 is a mitochondrial protein with distinct functional properties. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:3305–3312. - PubMed
-
- Montesano Gesualdi N, Chirico G, Catanese MT, Pirozzi G, Esposito F. AROS-29 is involved in adaptive response to oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 2006;40:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Montesano Gesualdi N, Chirico G, Pirozzi G, Costantino E, Landriscina M, Esposito F. Tumor necrosis factor-associated protein 1 (TRAP-1) protects cells from oxidative stress and apoptosis. Stress. 2007;10:342–350. - PubMed
-
- Costantino E, Maddalena F, Calise S, Piscazzi A, Tirino V, Fersini A, et al. TRAP1, a novel mitochondrial chaperone responsible for multi-drug resistance and protection from apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2009;279:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

