Regenerating islet-derived 3-alpha is a biomarker of gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 21979939
- PMCID: PMC3242723
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-375006
Regenerating islet-derived 3-alpha is a biomarker of gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
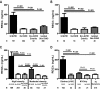
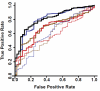
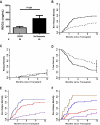
There are no plasma biomarkers specific for GVHD of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the GVHD target organ most associated with nonrelapse mortality (NRM) following hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Using an unbiased, large-scale, quantitative proteomic discovery approach to identify candidate biomarkers that were increased in plasma from HCT patients with GI GVHD, 74 proteins were increased at least 2-fold; 5 were of GI origin. We validated the lead candidate, REG3α, by ELISA in samples from 1014 HCT patients from 3 transplantation centers. Plasma REG3α concentrations were 3-fold higher in patients at GI GVHD onset than in all other patients and correlated most closely with lower GI GVHD. REG3α concentrations at GVHD onset predicted response to therapy at 4 weeks, 1-year NRM, and 1-year survival (P ≤ .001). In a multivariate analysis, advanced clinical stage, severe histologic damage, and high REG3α concentrations at GVHD diagnosis independently predicted 1-year NRM, which progressively increased with higher numbers of onset risk factors present: 25% for patients with 0 risk factors to 86% with 3 risk factors present (P < .001). REG3α is a plasma biomarker of GI GVHD that can be combined with clinical stage and histologic grade to improve risk stratification of patients.
Figures
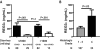
References
-
- Cutler C, Antin JH. Manifestation and treatment of acute graft-versus-host-disease. In: Appelbaum F, Forman SJ, Negrin RS, Blume KG, editors. Thomas' Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2009. pp. 1287–1303.
-
- Welniak LA, Blazar BR, Murphy WJ. Immunobiology of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:139–170. - PubMed
-
- Mowat A, Socie G. Intestinal graft-vs.-host disease. In: Ferrara JLM, Cooke KR, Deeg HJ, editors. Graft-vs-Host Disease. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 2004. pp. 279–327.
-
- Martin PJ, McDonald GB, Sanders JE, et al. Increasingly frequent diagnosis of acute gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2004;10(5):320–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

