A zebrafish transgenic model of Ewing's sarcoma reveals conserved mediators of EWS-FLI1 tumorigenesis
- PMID: 21979944
- PMCID: PMC3255547
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.007401
A zebrafish transgenic model of Ewing's sarcoma reveals conserved mediators of EWS-FLI1 tumorigenesis
Abstract
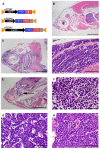
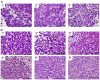
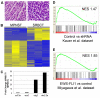
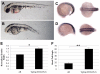
Ewing's sarcoma, a malignant bone tumor of children and young adults, is a member of the small-round-blue-cell tumor family. Ewing's sarcoma family tumors (ESFTs), which include peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs), are characterized by chromosomal translocations that generate fusions between the EWS gene and ETS-family transcription factors, most commonly FLI1. The EWS-FLI1 fusion oncoprotein represents an attractive therapeutic target for treatment of Ewing's sarcoma. The cell of origin of ESFT and the molecular mechanisms by which EWS-FLI1 mediates tumorigenesis remain unknown, and few animal models of Ewing's sarcoma exist. Here, we report the use of zebrafish as a vertebrate model of EWS-FLI1 function and tumorigenesis. Mosaic expression of the human EWS-FLI1 fusion protein in zebrafish caused the development of tumors with histology strongly resembling that of human Ewing's sarcoma. The incidence of tumors increased in a p53 mutant background, suggesting that the p53 pathway suppresses EWS-FLI1-driven tumorigenesis. Gene expression profiling of the zebrafish tumors defined a set of genes that might be regulated by EWS-FLI1, including the zebrafish ortholog of a crucial EWS-FLI1 target gene in humans. Stable zebrafish transgenic lines expressing EWS-FLI1 under the control of the heat-shock promoter exhibit altered embryonic development and defective convergence and extension, suggesting that EWS-FLI1 interacts with conserved developmental pathways. These results indicate that functional targets of EWS-FLI1 that mediate tumorigenesis are conserved from zebrafish to human and provide a novel context in which to study the function of this fusion oncogene.
Figures

References
-
- Amatruda J. F., Patton E. E. (2008). Genetic models of cancer in zebrafish. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 271, 1–34 - PubMed
-
- Baer C., Nees M., Breit S., Selle B., Kulozik A. E., Schaefer K. L., Braun Y., Wai D., Poremba C. (2004). Profiling and functional annotation of mRNA gene expression in pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 110, 687–694 - PubMed
-
- Baird K., Davis S., Antonescu C. R., Harper U. L., Walker R. L., Chen Y., Glatfelter A. A., Duray P. H., Meltzer P. S. (2005). Gene expression profiling of human sarcomas: insights into sarcoma biology. Cancer Res. 65, 9226–9235 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

