Universal stress proteins are important for oxidative and acid stress resistance and growth of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 21980369
- PMCID: PMC3184099
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024965
Universal stress proteins are important for oxidative and acid stress resistance and growth of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Pathogenic bacteria maintain a multifaceted apparatus to resist damage caused by external stimuli. As part of this, the universal stress protein A (UspA) and its homologues, initially discovered in Escherichia coli K-12 were shown to possess an important role in stress resistance and growth in several bacterial species.
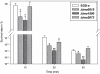
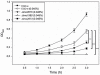
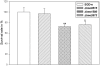
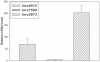
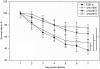
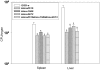
Methods and findings: We conducted a study to assess the role of three homologous proteins containing the UspA domain in the facultative intracellular human pathogen Listeria monocytogenes under different stress conditions. The growth properties of three UspA deletion mutants (Δlmo0515, Δlmo1580 and Δlmo2673) were examined either following challenge with a sublethal concentration of hydrogen peroxide or under acidic conditions. We also examined their ability for intracellular survival within murine macrophages. Virulence and growth of usp mutants were further characterized in invertebrate and vertebrate infection models. Tolerance to acidic stress was clearly reduced in Δlmo1580 and Δlmo0515, while oxidative stress dramatically diminished growth in all mutants. Survival within macrophages was significantly decreased in Δlmo1580 and Δlmo2673 as compared to the wild-type strain. Viability of infected Galleria mellonella larvae was markedly higher when injected with Δlmo1580 or Δlmo2673 as compared to wild-type strain inoculation, indicating impaired virulence of bacteria lacking these usp genes. Finally, we observed severely restricted growth of all chromosomal deletion mutants in mice livers and spleens as compared to the load of wild-type bacteria following infection.
Conclusion: This work provides distinct evidence that universal stress proteins are strongly involved in listerial stress response and survival under both in vitro and in vivo growth conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Divergent evolution of the activity and regulation of the glutamate decarboxylase systems in Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e and 10403S: roles in virulence and acid tolerance.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 11;9(11):e112649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112649. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25386947 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA chaperone Hfq is a novel regulator of catalase expression and hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress response in Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Feb 1;227:103-116. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.11.038. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39608557
-
Loss of SigB in Listeria monocytogenes Strains EGD-e and 10403S Confers Hyperresistance to Hydrogen Peroxide in Stationary Phase under Aerobic Conditions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Jul 15;82(15):4584-4591. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00709-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27208116 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Universal Stress Proteins in Bacterial Infections.Curr Med Chem. 2017 Nov 24;24(36):3970-3979. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170124145543. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28120710 Review.
-
Structures, functions, and regulatory networks of universal stress proteins in clinically relevant pathogenic Bacteria.Cell Signal. 2024 Apr;116:111032. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.111032. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38185228 Review.
Cited by
-
Parasite Survival and Disease Persistence in Cystic Fibrosis, Schistosomiasis and Pathogenic Bacterial Diseases: A Role for Universal Stress Proteins?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 8;22(19):10878. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910878. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A detailed view of the intracellular transcriptome of Listeria monocytogenes in murine macrophages using RNA-seq.Front Microbiol. 2015 Oct 30;6:1199. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01199. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26579105 Free PMC article.
-
The DegU Orphan Response Regulator Contributes to Heat Stress Resistance in Listeria monocytogenes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Dec 13;11:761335. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.761335. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34966695 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial efficacy interference of the photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticle and the lytic bacteriophage vb_EcoS_bov25_1D on the Enterohaemorragic Escherichia coli strain Sakai.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(14):e33562. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33562. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108916 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory network features in Listeria monocytogenes-changing the way we talk.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Feb 14;4:14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00014. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24592357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kvint K, Nachin L, Diez A, Nystrom T. The bacterial universal stress protein: function and regulation. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6:140–145. - PubMed
-
- O'Toole R, Williams HD. Universal stress proteins and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 2003;154:387–392. - PubMed
-
- Sousa MC, McKay DB. Structure of the universal stress protein of Haemophilus influenzae. Structure. 2001;9:1135–1141. - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann RD, Adams MD, White O, Clayton RA, Kirkness EF, et al. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science. 1995;269:496–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

