The SOCS2 ubiquitin ligase complex regulates growth hormone receptor levels
- PMID: 21980433
- PMCID: PMC3183054
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025358
The SOCS2 ubiquitin ligase complex regulates growth hormone receptor levels
Abstract
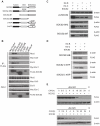
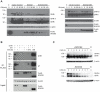
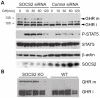
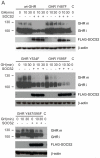
Growth Hormone is essential for the regulation of growth and the homeostatic control of intermediary metabolism. GH actions are mediated by the Growth Hormone Receptor; a member of the cytokine receptor super family that signals chiefly through the JAK2/STAT5 pathway. Target tissue responsiveness to GH is under regulatory control to avoid excessive and off-target effects upon GHR activation. The suppressor of cytokine signalling 2 (SOCS) is a key regulator of GHR sensitivity. This is clearly shown in mice where the SOCS2 gene has been inactivated, which show 30-40% increase in body length, a phenotype that is dependent on endogenous GH secretion. SOCS2 is a GH-stimulated, STAT5b-regulated gene that acts in a negative feedback loop to downregulate GHR signalling. Since the biochemical basis for these actions is poorly understood, we studied the molecular function of SOCS2. We demonstrated that SOCS2 is part of a multimeric complex with intrinsic ubiquitin ligase activity. Mutational analysis shows that the interaction with Elongin B/C controls SOCS2 protein turnover and affects its molecular activity. Increased GHR levels were observed in livers from SOCS2⁻/⁻ mice and in the absence of SOCS2 in in vitro experiments. We showed that SOCS2 regulates cellular GHR levels through direct ubiquitination and in a proteasomally dependent manner. We also confirmed the importance of the SOCS-box for the proper function of SOCS2. Finally, we identified two phosphotyrosine residues in the GHR to be responsible for the interaction with SOCS2, but only Y487 to account for the effects of SOCS2. The demonstration that SOCS2 is an ubiquitin ligase for the GHR unveils the molecular basis for its physiological actions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Deng L, He K, Wang X, Yang N, Thangavel C, et al. Determinants of growth hormone receptor down-regulation. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:1537–1551. - PubMed
-
- Tritos NA, Biller BM. Growth hormone and bone. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2009;16:415–422. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SF, Farquharson C. The effect of GH and IGF1 on linear growth and skeletal development and their modulation by SOCS proteins. J Endocrinol. 2010;206:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Greenhalgh CJ, Bertolino P, Asa SL, Metcalf D, Corbin JE, et al. Growth enhancement in suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS-2)-deficient mice is dependent on signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b). Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:1394–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

