Human cysteine cathepsins are not reliable markers of infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 21980493
- PMCID: PMC3182231
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025577
Human cysteine cathepsins are not reliable markers of infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis
Abstract
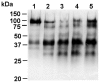
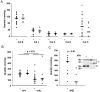
Cysteine cathepsins have emerged as new players in inflammatory lung disorders. Their activities are dramatically increased in the sputum of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, suggesting that they are involved in the pathophysiology of CF. We have characterized the cathepsins in CF expectorations and evaluated their use as markers of colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The concentrations of active cathepsins B, H, K, L and S were the same in P. aeruginosa-positive (19 Ps+) and P. aeruginosa-negative (6 Ps-) samples, unlike those of human neutrophil elastase. Also the cathepsin inhibitory potential and the cathepsins/cathepsin inhibitors imbalance remained unchanged and similar (∼2-fold) in the Ps+ and Ps- groups (p<0.001), which correlated with the breakdown of their circulating cystatin-like inhibitors (kininogens). Procathepsins, which may be activated autocatalytically, are a potential proteolytic reservoir. Immunoblotting and active-site labeling identified the double-chain cathepsin B, the major cathepsin in CF sputum, as the main molecular form in both Ps+ and Ps- samples, despite the possible release of the ∼31 kDa single-chain form from procathepsin B by sputum elastase. Thus, the hydrolytic activity of cysteine cathepsins was not correlated with bacterial colonization, indicating that cathepsins, unlike human neutrophil elastase, are not suitable markers of P. aeruginosa infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

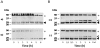
References
-
- Kerem B, Rommens JM, Buchanan JA, Markiewicz D, Cox TK, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989;245:1073–1080. - PubMed
-
- Riordan JR, Rommens JM, Kerem B, Alon N, Rozmahel R, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989;245:1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Grasemann H, Ratjen F. Emerging therapies for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2010;15:653–659. - PubMed
-
- Pham CT. Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:541–550. - PubMed
-
- Korkmaz B, Moreau T, Gauthier F. Neutrophil elastase, proteinase 3 and cathepsin G: physicochemical properties, activity and physiopathological functions. Biochimie. 2008;90:227–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

