Post-Golgi supramolecular assembly of aquaporin-4 in orthogonal arrays
- PMID: 21981006
- PMCID: PMC3319398
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01299.x
Post-Golgi supramolecular assembly of aquaporin-4 in orthogonal arrays
Abstract
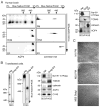
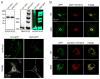
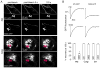
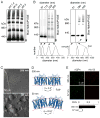
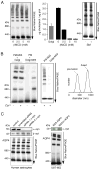
The supramolecular assembly of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in orthogonal arrays of particles (OAPs) involves N-terminus interactions of the M23-AQP4 isoform. We found AQP4 OAPs in cell plasma membranes but not in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or Golgi, as shown by: (i) native gel electrophoresis of brain and AQP4-transfected cells, (ii) photobleaching recovery of green fluorescent protein-AQP4 chimeras in live cells and (iii) freeze-fracture electron microscopy (FFEM). We found that AQP4 OAP formation in plasma membranes, but not in the Golgi, was not related to AQP4 density, pH, membrane lipid composition, C-terminal PDZ domain interactions or α-syntrophin expression. Remarkably, however, fusion of AQP4-containing Golgi vesicles with (AQP4-free) plasma membrane vesicles produced OAPs, suggesting the involvement of plasma membrane factor(s) in AQP4 OAP formation. In investigating additional possible determinants of OAP assembly we discovered membrane curvature-dependent OAP assembly, in which OAPs were disrupted by extrusion of plasma membrane vesicles to ∼110 nm diameter, but not to ∼220 nm diameter. We conclude that AQP4 supramolecular assembly in OAPs is a post-Golgi phenomenon involving plasma membrane-specific factor(s). Post-Golgi and membrane curvature-dependent OAP assembly may be important for vesicle transport of AQP4 in the secretory pathway and AQP4-facilitated astrocyte migration, and suggests a novel therapeutic approach for neuromyelitis optica.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures
References
-
- Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Umenishi F, Kawashima M, Brown D, Verkman AS. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J Cell Sci. 1995;108 (Pt 9):2993–3002. - PubMed
-
- Verkman AS, Binder DK, Bloch O, Auguste K, Papadopoulos MC. Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1085–1093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK86125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK086125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

