Effects of prolonged vaginal distension and β-aminopropionitrile on urinary continence and urethral structure
- PMID: 21982017
- PMCID: PMC3191886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.07.1381
Effects of prolonged vaginal distension and β-aminopropionitrile on urinary continence and urethral structure
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of prolonged vaginal distension and β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN) on the urinary patterns and urethral structure in female virgin rats.
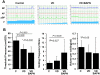
Methods: A total of 21 female virgin rats were randomly divided into 3 groups of 7 rats each. The control group received no intervention; the vaginal distension (VD) group was treated with prolonged VD by balloon inflation; and the VD plus BAPN group was treated with VD plus intraperitoneal injection of 150 mg/kg of BAPN every 3 days. Three weeks later, all the rats underwent conscious cystometric analysis and were then killed for histologic analysis of the urethra.
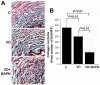
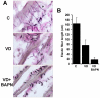
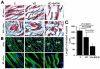
Results: Conscious cystometry identified 0, 3, and 5 rats in the control, VD, and VD plus BAPN groups with an abnormal voiding pattern, respectively. The urethral collagen content was significantly lower in the VD and VD plus BAPN rats compared with the control rats. The urethral elastic fibers were disorganized and shorter in the VD and VD plus BAPN rats and were fragmented and lacking the intermuscle connections in the VD plus BAPN rats. The urethral striated muscle fibers were shorter and more widely spaced in the VD and VD plus BAPN rats than in the control rats. Additionally, those in the VD plus BAPN group exhibited an abnormal wavy shape suggestive of a lack of architectural support.
Conclusion: Prolonged vaginal distension caused urodynamic changes and histologic abnormalities in the urethra, including reduced collagen content, fragmented elastic fibers, and sparsely arranged and shortened striated muscle fibers. BAPN appears to interfere with the restoration of collagen and elastic fibers.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microenergy acoustic pulse therapy restores urethral wall integrity and continence in a rat model of female stress incontinence.Neurourol Urodyn. 2022 Aug;41(6):1323-1335. doi: 10.1002/nau.24939. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Neurourol Urodyn. 2022. PMID: 35451520 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Treatment With Low-intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in an Irreversible Rat Model of Stress Urinary Incontinence.Urology. 2020 Jul;141:187.e1-187.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.03.035. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Urology. 2020. PMID: 32283169 Free PMC article.
-
Time course for urethral neuromuscular reestablishment and its facilitated recovery by transcutaneous neuromodulation after simulated birth trauma in rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 3;11(1):21591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01200-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34732833 Free PMC article.
-
Increased duration of simulated childbirth injuries results in increased time to recovery.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):R1738-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00784.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17204590 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of continence reflexes by dynamic urethral pressure recordings in a rat stress urinary incontinence model induced by multiple simulated birth traumas.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):F781-F788. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00197.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31313954 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cell-based secondary prevention of childbirth-induced pelvic floor trauma.Nat Rev Urol. 2017 Jun;14(6):373-385. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.42. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Nat Rev Urol. 2017. PMID: 28374792 Review.
-
Stem cell therapy for stress urinary incontinence: a critical review.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Apr 10;21(6):834-43. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0621. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22121849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of balloon tamponade in management of vaginal laceration and its possible complication of urinary stress incontinence: a case report.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-02885-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32293311 Free PMC article.
-
Microenergy shockwave therapies for female stress urinary incontinence.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):1687-1694. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-9. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39280672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-Related Changes in Urethral Structure and Responds to Injury: Single-Cell Atlas of a Rat Model of Vaginal Birth Injury induced Stress Urinary Incontinence.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 12:rs.3.rs-3901406. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3901406/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38410468 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Norton P, Brubaker L. Urinary incontinence in women. Lancet. 2006;367:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Hu TW, Wagner TH, Bentkover JD, et al. Costs of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in the United States: a comparative study. Urology. 2004;63:461–465. - PubMed
-
- Dooley Y, Kenton K, Cao G, et al. Urinary Incontinence Prevalence: Results From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Urol. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Yang JM. Factors affecting urethrocystographic parameters in urinary continent women. J Clin Ultrasound. 1996;24:249–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

