Rod vision is controlled by dopamine-dependent sensitization of rod bipolar cells by GABA
- PMID: 21982372
- PMCID: PMC3197016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.030
Rod vision is controlled by dopamine-dependent sensitization of rod bipolar cells by GABA
Abstract
Dark and light adaptation of retinal neurons allow our vision to operate over an enormous light intensity range. Here we report a mechanism that controls the light sensitivity and operational range of rod-driven bipolar cells that mediate dim-light vision. Our data indicate that the light responses of these cells are enhanced by sustained chloride currents via GABA(C) receptor channels. This sensitizing GABAergic input is controlled by dopamine D1 receptors, with horizontal cells serving as a plausible source of GABA release. Our findings expand the role of dopamine in vision from its well-established function of suppressing rod-driven signals in bright light to enhancing the same signals under dim illumination. They further reveal a role for GABA in sensitizing the circuitry for dim-light vision, thereby complementing GABA's traditional role in providing dynamic feedforward and feedback inhibition in the retina.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
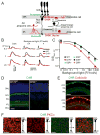




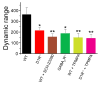
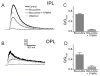
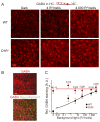
References
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. Homomeric rho 1 GABA channels: activation properties and domains. Receptors Channels. 1994;2:227–236. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A, Waters N, Holm-Waters S, Tedroff J, Nilsson M, Carlsson ML. Interactions between monoamines, glutamate, and GABA in schizophrenia: new evidence. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:237–260. - PubMed
-
- Deniz S, Wersinger E, Schwab Y, Mura C, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Rendon A, Sahel JA, Picaud S, Roux MJ. Mammalian retinal horizontal cells are unconventional GABAergic neurons. J Neurochem. 2011;116:350–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH073853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 EY018131/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY010336/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 EY006671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY10336/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY06671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH073853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014701/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY5722/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY007551/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MH073853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY005722/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY006671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY014701/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

