3-epi-25 hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are not correlated with age in a cohort of infants and adults
- PMID: 21983164
- PMCID: PMC3236660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2011.09.028
3-epi-25 hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are not correlated with age in a cohort of infants and adults
Abstract
Background: The implementation of mass spectrometry to measure serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentrations has led to concerns regarding the measurement and reporting of the C3-epimer of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) [3-epi-25(OH)D(3)], for which there is a near-total lack of data regarding its clinical significance.
Methods: We developed a chromatographic method to resolve (>90%) 3-epi-25(OH)D(3) from 25(OH)D(3) using a pentafluorophenyl propyl chromatographic column. Using LC-MS/MS, we determined the serum concentrations of 25(OH)D(3) and 3-epi-25(OH)D(3) in 626 patients aged 3 days to 94 years undergoing routine vitamin D testing.
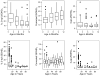
Results: Comparison between DiaSorin RIA and the new LC-MS/MS method for total 25(OH)D had acceptable agreement. Our data indicate an increase in 25(OH)D(3) rather than a reduction in epimer concentration. An average of 3.3 ng/ml of 3-epi-25(OH)D(3) was detected in adolescents and adults. Inclusion of 3-epi-25(OH)D(3) in the total 25(OH)D(3) concentration resulted in 9% (<1 year) and 3% (1 to 94 years) potential misclassification of patients as vitamin D sufficient.
Conclusions: The new LC-MS/MS method is capable of chromatographically separating 25(OH)D(3) and 3-epi-25(OH)D(3). It was used to confirm that the contribution of 3-epi-25OHD(3) to total 25OHD(3) concentrations decreases with age in infants and is detectable in adults.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Singh RJ, Taylor RL, Reddy GS, Grebe SKG. C-3 epimers can account for a significant proportion of total circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D in infants, complicating accurate measurement and interpretation of vitamin D status. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2006;91:3055–3061. - PubMed
-
- Fleet JC, Bradley J, Reddy GS, Ray R, Wood RJ. 1 alpha,25-(OH)2-vitamin D3 analogs with minimal in vivo calcemic activity can stimulate significant transepithelial calcium transport and mRNA expression in vitro. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 1996;329:228–234. - PubMed
-
- Brown AJ, Ritter C, Slatopolsky E, Muralidharan KR, Okamura WH, Reddy GS. 1Alpha,25-dihydroxy-3-epi-vitamin D3, a natural metabolite of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is a potent suppressor of parathyroid hormone secretion. J Cell Biochem. 1999;73:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Schleicher RL, Encisco SE, Chaudhary-Webb M, Paliakov E, McCoy LF, Pfeiffer CM. Isotope dilution ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D2, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412:1594–1599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

