Deep resequencing of GWAS loci identifies independent rare variants associated with inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 21983784
- PMCID: PMC3378381
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.952
Deep resequencing of GWAS loci identifies independent rare variants associated with inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
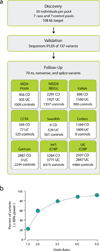
More than 1,000 susceptibility loci have been identified through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of common variants; however, the specific genes and full allelic spectrum of causal variants underlying these findings have not yet been defined. Here we used pooled next-generation sequencing to study 56 genes from regions associated with Crohn's disease in 350 cases and 350 controls. Through follow-up genotyping of 70 rare and low-frequency protein-altering variants in nine independent case-control series (16,054 Crohn's disease cases, 12,153 ulcerative colitis cases and 17,575 healthy controls), we identified four additional independent risk factors in NOD2, two additional protective variants in IL23R, a highly significant association with a protective splice variant in CARD9 (P < 1 × 10(-16), odds ratio ≈ 0.29) and additional associations with coding variants in IL18RAP, CUL2, C1orf106, PTPN22 and MUC19. We extend the results of successful GWAS by identifying new, rare and probably functional variants that could aid functional experiments and predictive models.
Figures


References
-
- Loftus EV., Jr Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(6):1504–1517. - PubMed
-
- Bengtson MB, et al. Familial aggregation in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in a Norwegian population-based cohort followed for ten years. J Crohns Colitis. 2008 Jun;3(2):92–99. - PubMed
-
- Brant SR. Update on the heritability of inflammatory bowel disease: the importance of twin studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010 Jan;17(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Rioux JD, Abbas AK. Paths to understanding the genetic basis of autoimmune disease. Nature. 2005;435(7042):584–589. - PubMed
-
- Nadeau JH. Single nucleotide polymorphisms: tackling complexity. Nature. 2002;420(6915):517–518. (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HG005923/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064869/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064869/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI062773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK086502/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HG005923/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060049/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK062422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK084554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI067152/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI065687/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK83756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ETM/75/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/540/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI065687/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 01038/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- DK060049/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DK84554-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK086502/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK062432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 AI067152/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

