miRNA repression involves GW182-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT through conserved W-containing motifs
- PMID: 21984184
- PMCID: PMC3885283
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2166
miRNA repression involves GW182-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT through conserved W-containing motifs
Abstract
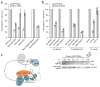
miRNA-mediated repression in animals is dependent on the GW182 protein family. GW182 proteins are recruited to the miRNA repression complex through direct interaction with Argonaute proteins, and they function downstream to repress target mRNA. Here we demonstrate that in human and Drosophila melanogaster cells, the critical repressive features of both the N-terminal and C-terminal effector domains of GW182 proteins are Gly/Ser/Thr-Trp (G/S/TW) or Trp-Gly/Ser/Thr (WG/S/T) motifs. These motifs, which are dispersed across both domains and act in an additive manner, function by recruiting components of the CCR4-NOT deadenylation complex. A heterologous yeast polypeptide with engineered WG/S/T motifs acquired the ability to repress tethered mRNA and to interact with the CCR4-NOT complex. These results identify previously unknown effector motifs functioning as important mediators of miRNA-induced silencing in both species, and they reveal that recruitment of the CCR4-NOT complex by tryptophan-containing motifs acts downstream of GW182 to repress mRNAs, including inhibiting translation independently of deadenylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

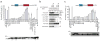
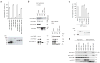

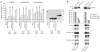
Comment in
-
New insights in the mechanism of microRNA-mediated target repression.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 4;18(11):1181-2. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2170. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22056803 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

