Hydrogen exchange during cell-free incorporation of deuterated amino acids and an approach to its inhibition
- PMID: 21984356
- PMCID: PMC3254145
- DOI: 10.1007/s10858-011-9575-4
Hydrogen exchange during cell-free incorporation of deuterated amino acids and an approach to its inhibition
Abstract
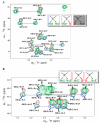
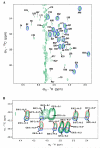
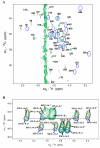
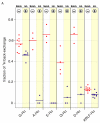
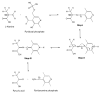
Perdeuteration, selective deuteration, and stereo array isotope labeling (SAIL) are valuable strategies for NMR studies of larger proteins and membrane proteins. To minimize scrambling of the label, it is best to use cell-free methods to prepare selectively labeled proteins. However, when proteins are prepared from deuterated amino acids by cell-free translation in H(2)O, exchange reactions can lead to contamination of (2)H sites by (1)H from the solvent. Examination of a sample of SAIL-chlorella ubiquitin prepared by Escherichia coli cell-free synthesis revealed that exchange had occurred at several residues (mainly at Gly, Ala, Asp, Asn, Glu, and Gln). We present results from a study aimed at identifying the exchanging sites and level of exchange and at testing a strategy for minimizing (1)H contamination during wheat germ cell-free translation of proteins produced from deuterated amino acids by adding known inhibitors of transaminases (1 mM aminooxyacetic acid) and glutamate synthetase (0.1 mM L: -methionine sulfoximine). By using a wheat germ cell-free expression system, we produced [U-(2)H, (15)N]-chlorella ubiquitin without and with added inhibitors, and [U-(15)N]-chlorella ubiquitin as a reference to determine the extent of deuterium incorporation. We also prepared a sample of [U-(13)C, (15)N]-chlorella ubiquitin, for use in assigning the sites of exchange. The added inhibitors did not reduce the protein yield and were successful in blocking hydrogen exchange at C(α) sites, with the exception of Gly, and at C(β) sites of Ala. We discovered, in addition, that partial exchange occurred with or without the inhibitors at certain side-chain methyl and methylene groups: Asn-H(β), Asp-H(β), Gln-H(γ), Glu-H(γ), and Lys-H(ε). The side-chain labeling pattern, in particular the mixed chiral labeling resulting from partial exchange at certain sites, should be of interest in studies of large proteins, protein complexes, and membrane proteins.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Improving yields of deuterated, methyl labeled protein by growing in H2O.J Biomol NMR. 2018 Aug;71(4):263-273. doi: 10.1007/s10858-018-0200-7. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Biomol NMR. 2018. PMID: 30073492 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha protons as NMR probes in deuterated proteins.J Biomol NMR. 2019 Feb;73(1-2):81-91. doi: 10.1007/s10858-019-00230-y. Epub 2019 Feb 14. J Biomol NMR. 2019. PMID: 30762170 Free PMC article.
-
A practical method for cell-free protein synthesis to avoid stable isotope scrambling and dilution.Anal Biochem. 2011 Apr 15;411(2):223-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2011.01.017. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Anal Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21256106
-
Selective labeling and unlabeling strategies in protein solid-state NMR spectroscopy.J Biomol NMR. 2018 Jul;71(3):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s10858-017-0156-z. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Biomol NMR. 2018. PMID: 29197975 Review.
-
Methyl groups as probes of supra-molecular structure, dynamics and function.J Biomol NMR. 2010 Jan;46(1):75-87. doi: 10.1007/s10858-009-9376-1. Epub 2009 Sep 27. J Biomol NMR. 2010. PMID: 19784810 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthetically directed ²H labelling for stereospecific resonance assignments of glycine methylene groups.J Biomol NMR. 2013 Jan;55(1):97-104. doi: 10.1007/s10858-012-9690-x. Epub 2012 Nov 29. J Biomol NMR. 2013. PMID: 23192292
-
Development of a cell-free protein synthesis system for practical use.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2021;97(5):261-276. doi: 10.2183/pjab.97.015. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33980755 Free PMC article.
-
Half a Century of Progress: The Evolution of Wheat Germ-Based In Vitro Translation into a Versatile Protein Production Method.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 10;26(8):3577. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083577. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid-State NMR for Studying the Structure and Dynamics of Viral Assemblies.Viruses. 2020 Sep 24;12(10):1069. doi: 10.3390/v12101069. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32987909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-free expression, purification, and membrane reconstitution for NMR studies of the nonstructural protein 4B from hepatitis C virus.J Biomol NMR. 2016 Jun;65(2):87-98. doi: 10.1007/s10858-016-0040-2. Epub 2016 May 27. J Biomol NMR. 2016. PMID: 27233794
References
-
- Bartels C, Xia TH, Billeter M, Güntert P, Wüthrich K. The program XEASY for computer-supported NMR spectral-analysis of biological macromolecules. J Biomol NMR. 1995;5:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A. NMRPIPE - A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR. 1995;6:277–293. - PubMed
-
- Etezady-Esfarjani T, Hiller S, Villalba C, Wüthrich K. Cell-free protein synthesis of perdeuterated proteins for NMR studies. J Biomol NMR. 2007;39:229–238. - PubMed
-
- Ikeya T, Takeda M, Yoshida H, Terauchi T, Jee JG, Kainosho M, Güntert P. Automated NMR structure determination of stereo-array isotope labeled ubiquitin from minimal sets of spectra using the SAIL-FLYA system. J Biomol NMR. 2009;44:261–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

